Puyuma language
| Puyuma | |
|---|---|
| Pinuyumayan | |
| Native to | Taiwan |
| Ethnicity | Puyuma people |
Native speakers | 8,500 (2002)[1] |
Language family | Austronesian
|
| Language codes | |
| ISO 639-3 | pyu |
| Glottolog | puyu1239 |
| ELP | Puyuma |
| Linguasphere | 30-JAA-a |
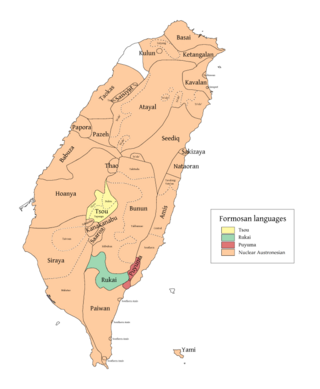 (red) Puyuma | |
 Puyuma is classified as Vulnerable by the UNESCO Atlas of the World's Languages in Danger | |
The Puyuma language or Pinuyumayan (Chinese: 卑南語; pinyin: Bēinányǔ), is the language of the Puyuma, an indigenous people of Taiwan. It is a divergent Formosan language of the Austronesian family. Most speakers are older adults.
Puyuma is one of the more divergent of the Austronesian languages and falls outside reconstructions of Proto-Austronesian.
Dialects
The internal classification of Puyuma dialects below is from Ting (1978). Nanwang Puyuma is considered to be the relatively phonologically conservative but grammatically innovative, as in it preserves proto-Puyuma voiced plosives but syncretizes the use of both oblique and genitive case.[2]
- Proto-Puyuma
- Nanwang
- (Main branch)
- Pinaski–Ulivelivek
- Pinaski
- Ulivelivek
- Rikavung
- Kasavakan–Katipul
- Kasavakan
- Katipul
- Pinaski–Ulivelivek
Puyuma-speaking villages are:[3]
- Puyuma cluster ('born of the bamboo')
- Puyuma (Chinese: Nanwang 南王)
- Apapulu (Chinese: Paosang 寶桑)
- Katipul cluster ('born of a stone')
- Alipai (Chinese: Pinlang 賓朗)
- Pinaski (Chinese: Hsia Pinlang 下賓朗); 2 km north of Puyuma/Nanwang, and maintains close relations with it
- Pankiu (Chinese: Pankiu 班鳩)
- Kasavakan (Chinese: Chienhe 建和)
- Katratripul (Chinese: Chihpen 知本)
- Likavung (Chinese: Lichia 利嘉)
- Tamalakaw (Chinese: Taian 泰安)
- Ulivelivek (Chinese: Chulu 初鹿)
Phonology
Puyuma has 18 consonants and 4 vowels:
| Bilabial | Alveolar | Retroflex | Palatal | Velar | Glottal | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Nasal | m | n | ŋ ⟨ng⟩ | ||||
| Plosive | Voiceless | p | t | ʈ ⟨tr⟩ | k | ʔ ⟨’⟩ | |
| Voiced | b | d | ɖ ⟨dr⟩ | ɡ | |||
| Fricative | s | ||||||
| Trill | r | ||||||
| Approximant | l ⟨lr⟩ | ɭ ⟨l⟩ | j ⟨y⟩ | w | |||
| Front | Central | Back | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Close | i | u | |
| Mid | ə ⟨e⟩ | ||
| Open | a |
Note that Teng uses ⟨lr⟩ for /ɭ/ and ⟨l⟩ for /l/, unlike in official version. The official orthography is used in this article.
Grammar
Morphology
Puyuma verbs have four types of focus:[5]
- Actor focus: Ø (no mark), -em-, -en- (after labials), me-, meʔ-, ma-
- Object focus: -aw
- Referent focus: -ay
- Instrumental focus: -anay
There are three verbal aspects:[5]
- Perfect
- Imperfect
- Future
There are two modes:[5]
- Imperative
- Hortative future
Affixes include:[5]
- Perfect: Ø (no mark)
- Imperfect: Reduplication; -a-
- Future: Reduplication, sometimes only -a-
- Hortative future: -a-
- Imperative mode: Ø (no mark)
| Active | Patient | Locative | Causative | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Realis | Unmarked | tremakaw | trakawaw | trakaway | trakawanay |
| Progressive | trematrakaw | tratrakawaw | tratrakaway | tratrakawanay | |
| Durative | trematratrakaw | tratratrakawaw | tratratrakaway | tratratrakawanay | |
| Irrealis | tratrakaw | tratrakawi | tratrakawan | ||
| Imperative | trakaw | trakawi | trakawu | trakawan | |
| Hortative | tremakawa | — | |||
Syntax
Puyuma has a verb-initial word order.
Articles include:[7]
- i – singular personal
- a – singular non-personal
- na – plural (personal and non-personal)
Pronouns
The Puyuma personal pronouns are:[8]
| Type of Pronoun | Nominative[9] | Oblique: Direct | Oblique: Indirect | Oblique: Non-Subject | Neutral |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1s. | nanku | kanku, kananku | draku, drananku | kanku | kuiku |
| 2s. | nanu | kanu, kananu | dranu, drananu | kanu | yuyu |
| 3s. | nantu | kantu, kanantu | dratu, dranantu | kantaw | taytaw |
| 1p. (incl.) | nanta | kanta, kananta | drata, drananta | kanta | taita |
| 1p. (excl.) | naniam | kaniam, kananiam | draniam, drananiam | kaniam | mimi |
| 2p. | nanemu | kanemu, kananemu | dranemu, drananemu | kanemu | muimu |
| 3p. | nantu | kantu, kanantu | dratu, dranantu | kantaw | – |
| Type of Pronoun | Nominative (Subject) | Nominative (Possessor of subject) | Genitive |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1s. | =ku | ku= | ku= |
| 2s. | =yu | nu= | nu= |
| 3s. | – | tu= | tu= |
| 1p. (incl.) | =ta | ta= | ta= |
| 1p. (excl.) | =mi | niam= | mi= |
| 2p. | =mu | mu= | mu= |
| 3p. | – | tu= | tu= |
Affixes
The Puyuma affixes are:[10]
- Prefixes
- ika-: the shape of; forming; shaping
- ka-: stative marker
- kara-: collective, to do something together
- kare-: the number of times
- ki-: to get something
- kir-: to go against (voluntarily)
- kitu-: to become
- kur-: be exposed to; be together (passively)
- m-, ma-: actor voice affix/intransitive affix
- maka-: along; to face against
- mara-: comparative/superlative marker
- mar(e)-: reciprocal; plurality of relations
- mi-: to have; to use
- mu-: anticausative marker
- mutu-: to become, to transform into
- pa-/p-: causative marker
- pu-: put
- puka-: ordinal numeral marker
- piya-: to face a certain direction
- si-: to pretend to
- tara-: to use (an instrument), to speak (a language)
- tinu-: to simulate
- tua-: to make, to form
- u-: to go
- ya-: to belong to; nominalizer
- Suffixes
- -a: perfective marker; numeral classifier
- -an: nominalizer; collective/plural marker
- -anay: conveyance voice affix/transitive affix
- -aw: patient voice affix/transitive affix
- -ay: locative voice affix/transitive affix
- -i, -u: imperative transitive marker
- Infixes
- -in-: perfective marker
- -em-: actor voice affix/intransitive affix
- Circumfixes
- -in-anan: the members of
- ka- -an: a period of time
- muri- -an: the way one is doing something; the way something was done
- sa- -an: people doing things together
- sa- -enan: people belonging to the same community
- si- -an: nominalizer
- Ca- -an, CVCV- -an: collectivity, plurality
Notes
- ^ Puyuma at Ethnologue (18th ed., 2015) (subscription required)
- ^ Teng (2009), pp. 839, 841.
- ^ Zeitoun & Cauquelin (2006), p. 655. sfnp error: no target: CITEREFZeitounCauquelin2006 (help)
- ^ a b Teng (2008), pp. 11, 18.
- ^ a b c d Cauquelin (2004), pp. 25–26.
- ^ Teng (2008), p. 112.
- ^ Cauquelin (1991), p. 27.
- ^ Teng (2008), pp. 61–64.
- ^ Possessor of subject
- ^ Teng (2008), pp. 282–285.
References
- Cauquelin, Josiane (1991). Dictionnaire puyuma-français. Paris: Ecole Française d'Extreme-Orient. ISBN 9782855395517.
- Cauquelin, Josiane (2004). Aborigines of Taiwan: The Puyuma – From Headhunting to the Modern World. London: RoutledgeCurzon. ISBN 9780203498590.
- Teng, Stacy Fang-ching (2007). A Reference Grammar of Puyuma, an Austronesian Language of Taiwan (Ph.D. thesis). doi:10.25911/5D63C47EE2628. hdl:1885/147042.
- Teng, Stacy Fang-ching (2008). A Reference Grammar of Puyuma, an Austronesian Language of Taiwan (PDF). Pacific Linguistics 595. Canberra: Pacific Linguistics, Research School of Pacific and Asian Studies, Australian National University. hdl:1885/28526. ISBN 9780858835870.
- Teng, Stacy Fang-ching (2009). "Case Syncretism in Puyuma" (PDF). Languages and Linguistics. 10 (4): 819–844. Archived from the original (PDF) on 2018-11-11.
- Ting, Pang-hsin (1978). "Reconstruction of Proto-Puyuma Phonology". Bulletin of the Institute of History and Philology. 49. Academia Sinica: 321–391. OCLC 4938029239. Archived from the original on 13 December 2014. Retrieved 5 December 2014.
- Teng, Fang-ching 鄧芳青 (2018). Bēinányǔ yǔfǎ gàilùn 卑南語語法概論 [Introduction to Puyuma Grammar] (in Chinese). Xinbei shi: Yuanzhu minzu weiyuanhui. ISBN 978-986-05-5694-0 – via alilin.apc.gov.tw.
External links
- Yuánzhùmínzú yǔyán xiànshàng cídiǎn 原住民族語言線上詞典 (in Chinese) – Puyuma search page at the "Aboriginal language online dictionary" website of the Indigenous Languages Research and Development Foundation
- Puyuma teaching and leaning materials published by the Council of Indigenous Peoples of Taiwan (in Chinese)
- Puyuma translation of President Tsai Ing-wen's 2016 apology to indigenous people – published on the website of the presidential office

- v
- t
- e
| Formosan |
| ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Malayo-Polynesian |
|
| Sinitic |
|
|---|
 | This Austronesian languages-related article is a stub. You can help Wikipedia by expanding it. |
- v
- t
- e










