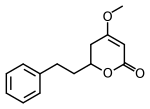
Dihydrokavain
 | |
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name 4-Methoxy-6-(2-phenylethyl)-5,6-dihydro-2H-pyran-2-one | |
| Other names Dihydrokawain Marindinin | |
| Identifiers | |
CAS Number |
|
3D model (JSmol) |
|
| ChemSpider |
|
PubChem CID |
|
| UNII |
|
CompTox Dashboard (EPA) |
|
InChI
| |
| |
| Properties | |
Chemical formula | C14H16O3 |
| Molar mass | 232.27 g/mol |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).  N verify (what is N verify (what is  Y Y N ?) N ?) Infobox references | |
Chemical compound
Dihydrokavain is one of the six major kavalactones found in the kava plant.[1] It appears to contribute significantly to the anxiolytic effects of kava, based on a study in chicks.[2]
Dihydrokavain bears some structural similarity to the strobilurins and has some fungicidal activity.[3]
An analogue of the molecule was also shown to improve glycemic control by modulating AMPK target genes expression in fruit flies.[4]
References
- ^ Malani, Joji (2002-12-03). "Evaluation of the effects of Kava on the Liver" (PDF). Fiji School of Medicine. Archived from the original (PDF) on 2009-03-20. Retrieved 2009-09-04.
- ^ Feltenstein, MW; LC Lambdin; M Ganzera; H Ranjith; W Dharmaratne; NP Nanayakkara; IA Khan; KJ Sufka (March 2003). "Anxiolytic properties of Piper methysticum extract samples and fractions in the chick social-separation-stress procedure". Phytotherapy Research. 17 (3): 210–216. doi:10.1002/ptr.1107. PMID 12672148. S2CID 10548965.
- ^ Zakharychev, Vladimir V; Kovalenko, Leonid V (1998-06-30). "Natural compounds of the strobilurin series and their synthetic analogues as cell respiration inhibitors". Russian Chemical Reviews. 67 (6): 535–544. Bibcode:1998RuCRv..67..535Z. doi:10.1070/rc1998v067n06abeh000426. ISSN 0036-021X. S2CID 95676421.
- ^ Hadiza Muhammad Maiturare; Mudassir Aliyu Magaji; Muhammad Kabiru Dallatu; Kabir Magaji Hamid; Mustapha Umar Imam; Ibrahim Malami (2022). "5,6-dehydrokawain improves glycaemic control by modulating AMPK target genes in Drosophila with a high-sucrose diet-induced hyperglycaemia". Phytomedicine Plus. 2 (2): 100261–. doi:10.1016/j.phyplu.2022.100261. ISSN 2667-0313. S2CID 247649601.
- v
- t
- e
Kava
| Kavalactones |
|
|---|---|
| Flavokavains | |
| Other |
 | This article about an anxiolytic is a stub. You can help Wikipedia by expanding it. |
- v
- t
- e










