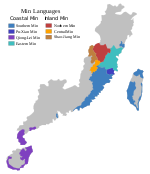
Zhenan Min
- Sinitic
- Chinese
- Min
- Coastal Min
- Southern Min
- Zhenan Min
- Southern Min
- Coastal Min
- Min
- Chinese
- Old Chinese[a]
- Proto-Min
mis)zhen123979-AAA-jb (transition to 79-AAA-h and -i)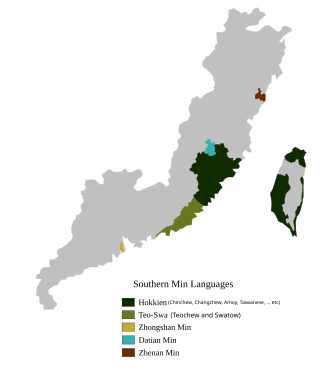
Zhenan Min (simplified Chinese: 浙南闽语; traditional Chinese: 浙南閩語; pinyin: Zhènán Mǐnyǔ; Pe̍h-ōe-jī: Chiat-lâm-bân-gí; lit. 'Min language in southern Zhejiang'), is a Min Nan Chinese language spoken in the vicinity of Wenzhou, in the southeast of Zhejiang province.
The Zhenan Min people had settled in areas such as Cangnan County, Pingyang County, Yuhuan County and Dongtou County from Fujian Province as early as the Tang dynasty period (618–907) and new waves of immigrants continued during the Southern Song dynasty, Ming dynasty and the Qing dynasty periods.
Zhenan Min has in the past been influenced by Eastern Min and the Northern Min, due to its close geographical proximity with those areas. It has limited intelligibility with other Min Nan dialects, such as Teochew and Hokkien–Taiwanese. Zhenan Min, in proximity to the Wenzhou dialect and Jinxiang dialect, has also borrowed some influences from Wu Chinese, such as voiced initials (z) and noun suffixes unique to Wu Chinese (such as 头).
Notes
References
- ^ Mei, Tsu-lin (1970), "Tones and prosody in Middle Chinese and the origin of the rising tone", Harvard Journal of Asiatic Studies, 30: 86–110, doi:10.2307/2718766, JSTOR 2718766
- ^ Pulleyblank, Edwin G. (1984), Middle Chinese: A study in Historical Phonology, Vancouver: University of British Columbia Press, p. 3, ISBN 978-0-7748-0192-8
- ^ Hammarström, Harald; Forkel, Robert; Haspelmath, Martin; Bank, Sebastian (2023-07-10). "Glottolog 4.8 - Min". Glottolog. Leipzig: Max Planck Institute for Evolutionary Anthropology. doi:10.5281/zenodo.7398962. Archived from the original on 2023-10-13. Retrieved 2023-10-13.
See also
- v
- t
- e
(Himachal, Uttarakhand, Nepal, Sikkim)
| Greater Magaric |
|---|

(Tibet, Bhutan, Arunachal)
| "Naga" | |
|---|---|
| Sal |
| Burmo-Qiangic |
|---|
(Arunachal)
| Greater Siangic |
|
|---|
 | This China-related article is a stub. You can help Wikipedia by expanding it. |
- v
- t
- e
 | This Sino-Tibetan languages-related article is a stub. You can help Wikipedia by expanding it. |
- v
- t
- e