Shao–Jiang Min
| Shao–Jiang | |
|---|---|
| 邵將 / 邵将 | |
| Native to | Southern China |
| Region | eastern Nanping Prefecture, Fujian |
Native speakers | 850,000 (2004)[1] |
Language family | Sino-Tibetan
|
Early forms | Proto-Sino-Tibetan
|
| Dialects |
|
| Language codes | |
| ISO 639-3 | None (mis) |
Linguist List | 1nn |
| Glottolog | shao1234 |
| Linguasphere | 79-AAA-l > 79-AAA-la |
 Shao–Jiang Min | |
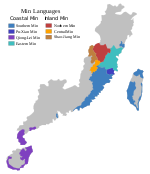
Shao–Jiang or Shaojiang Min (simplified Chinese: 邵将; traditional Chinese: 邵將; pinyin: Shàojiāng) is a Min Chinese language centered on Western Nanping in Northwest Fujian, specifically in the Nanping counties of Guangze, Shaowu, and Western Shunchang and the Northern Sanming county of Jiangle.
Shao–Jiang developed from Northern Min (Min Bei), and was deeply influenced by Gan Chinese and Hakka Chinese. The classification of Shao–Jiang is disputed. It is frequently classified as a dialect of Northern Min, but sometimes it is excluded from Min and classified as Gan Chinese instead. But it is mutually intelligible with neither other Northern Min nor other Gan. Actually it is a collection of dialects which have limited mutual intelligibility instead of a language. Some Chinese scholars call it Min-Gan dialects (闽赣方言), Min-Gan transition dialects (闽赣过渡方言) or Min-Hakka-Gan transition dialects (闽客赣过渡方言).
Notes
References
- ^ Language atlas of China (2nd edition), City University of Hong Kong, 2012, ISBN 978-7-10-007054-6.
- ^ Mei, Tsu-lin (1970), "Tones and prosody in Middle Chinese and the origin of the rising tone", Harvard Journal of Asiatic Studies, 30: 86–110, doi:10.2307/2718766, JSTOR 2718766
- ^ Pulleyblank, Edwin G. (1984), Middle Chinese: A study in Historical Phonology, Vancouver: University of British Columbia Press, p. 3, ISBN 978-0-7748-0192-8
- ^ Hammarström, Harald; Forkel, Robert; Haspelmath, Martin; Bank, Sebastian (2023-07-10). "Glottolog 4.8 - Min". Glottolog. Leipzig: Max Planck Institute for Evolutionary Anthropology. doi:10.5281/zenodo.7398962. Archived from the original on 2023-10-13. Retrieved 2023-10-13.
- Min Shaojiang dialect classification at Glossika
- v
- t
- e
(Himachal, Uttarakhand, Nepal, Sikkim)
| Greater Magaric |
|---|

(Tibet, Bhutan, Arunachal)
| "Naga" | |
|---|---|
| Sal |
| Burmo-Qiangic |
|---|
(Arunachal)
| Greater Siangic |
|
|---|