Trabecular meshwork
| Trabecular meshwork | |
|---|---|
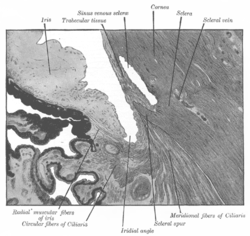 Enlarged general view of the iridial angle. (When enlarged, visible with older label of 'trabecular tissue') | |
| Details | |
| Identifiers | |
| Latin | reticulum trabeculare sclerae |
| MeSH | D014129 |
| Anatomical terminology [edit on Wikidata] | |



The trabecular meshwork is an area of tissue in the eye located around the base of the cornea, near the ciliary body, and is responsible for draining the aqueous humor from the eye via the anterior chamber (the chamber on the front of the eye covered by the cornea).
The tissue is spongy and lined by trabeculocytes; it allows fluid to drain into a set of tubes called Schlemm's canal which is lined by endothelium with blood and lymphatic properties that allow aqueous humor to flow into the blood system.[1]
Structure
The meshwork is divided up into three parts, with characteristically different ultrastructures:
- Inner uveal meshwork - Closest to the anterior chamber angle, contains thin cord-like trabeculae, orientated predominantly in a radial fashion, enclosing trabeculae spaces larger than the corneoscleral meshwork.
- Corneoscleral meshwork - Contains a large amount of elastin, arranged as a series of thin, flat, perforated sheets arranged in a laminar pattern; considered the ciliary muscle tendon.[2]
- Juxtacanalicular tissue (also known as the cribriform meshwork) - Lies immediately adjacent to Schlemm's canal, composed of connective tissue ground substance full of glycoaminoglycans and glycoproteins. This thin strip of tissue is covered by a monolayer of endothelial cells.
The trabecular meshwork is assisted to a small degree in the drainage of aqueous humour by a second outflow pathway, the uveo-scleral pathway (5-10% of outflow occurs this way). The uveo-scleral pathway is increased with the use of glaucoma drugs such as prostaglandins (e.g., Xalatan, Travatan).
The trabecular meshwork had previously been thought to arise from a point (apex) corresponding to the termination of the DM (Schwalbe's line) however it is now considered to extend into the cornea, forming the Dua's layer.[3]
Clinical significance
Glaucoma
It is thought that most cases of glaucoma (although not all) are caused or enabled by an increase in intraocular pressure. Pressure increases either when too much aqueous humor fluid is produced or by decreased aqueous humor outflow. The trabecular meshwork is responsible for most of the outflow of aqueous humor. When outflow is blocked, interventions such as trabeculectomy, trabeculoplasty, or aqueous shunt may be required to restore it.
See also
References
- ^ Karpinich NO, Caron KM (September 2014). "Schlemm's canal: more than meets the eye, lymphatics in disguise". The Journal of Clinical Investigation. 124 (9): 3701–3. doi:10.1172/JCI77507. PMC 4151199. PMID 25061871.
- ^ Sampaolesi R, Sampaolesi JR, Zárate J (2009). "Ocular Embryology with Special Reference to Chamber Angle Development". The Glaucomas. Berlin Heidelberg: Springer-Verlag. pp. 61–9. doi:10.1007/978-3-540-69146-4_8. ISBN 978-3-540-69144-0.
- ^ Dua HS, Faraj LA, Branch MJ, Yeung AM, Elalfy MS, Said DG, et al. (May 2014). "The collagen matrix of the human trabecular meshwork is an extension of the novel pre-Descemet's layer (Dua's layer)". The British Journal of Ophthalmology. 98 (5): 691–7. doi:10.1136/bjophthalmol-2013-304593. PMID 24532799.
External links
- Histology image: 08005loa – Histology Learning System at Boston University
- Diagram at glaucoma-association.com
- v
- t
- e
(outer)
| Sclera |
|
|---|---|
| Cornea |

tunic (middle)
| Choroid | |
|---|---|
| Ciliary body | |
| Iris |
| Layers | |
|---|---|
| Cells |
|
| Other |
of the eye
| Anterior segment | |
|---|---|
| Posterior segment |
- Keratocytes
- Ocular immune system
- Optical coherence tomography
- Eye care professional
- Eye disease
- Refractive error
- Accommodation
- Physiological Optics
- Visual perception










