Perifovea
Region in the retina

Perifovea is a region in the retina that circumscribes the parafovea and fovea and is a part of the macula lutea.[1] The perifovea is a belt that covers a 10° radius around the fovea and is 1.5 mm wide.[2][3] The perifovea ends when the Henle's fiber layer disappears and the ganglion cells are one-layered.[4]
Additional images
-
 Schematic diagram of the macula lutea of the retina, showing perifovea, parafovea, fovea, and clinical macula
Schematic diagram of the macula lutea of the retina, showing perifovea, parafovea, fovea, and clinical macula -
 Time-Domain OCT of the macular area of a retina at 800 nm, axial resolution 3 µm
Time-Domain OCT of the macular area of a retina at 800 nm, axial resolution 3 µm -
 Spectral-Domain OCT macula cross-section scan.
Spectral-Domain OCT macula cross-section scan. -
 macula histology (OCT)
macula histology (OCT) -
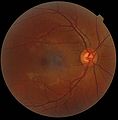 A fundus photograph showing the macula as a spot to the left. The optic disc is the area on the right where blood vessels converge. The grey, more diffuse spot in the centre is a shadow artifact.
A fundus photograph showing the macula as a spot to the left. The optic disc is the area on the right where blood vessels converge. The grey, more diffuse spot in the centre is a shadow artifact.
See also
- Eye movements in reading
- Fixation (visual)
- Optical coherence tomography (OCT)
References
- ^ Myron Yanoff; Jay S. Duker (6 November 2013). Ophthalmology: Expert Consult: Online and Print. Elsevier Health Sciences. p. 421. ISBN 978-1-4557-5001-6.
- ^ Jasjit S. Suri (2008). Image Modeling of the Human Eye. Artech House. p. 133. ISBN 978-1-59693-209-8.
- ^ Vito Roberto (10 November 1993). Intelligent Perceptual Systems: New Directions in Computational Perception. Springer. p. 347. ISBN 978-3-540-57379-1.
- ^ Louis E. Probst; Julie H. Tsai; George Goodman (OD.) (2012). Ophthalmology: Clinical and Surgical Principles. SLACK Incorporated. p. 28. ISBN 978-1-55642-735-0.
- v
- t
- e

















