| RBPJ |
|---|
 |
| Available structures |
|---|
| PDB | Ortholog search: PDBe RCSB |
|---|
| List of PDB id codes |
|---|
2F8X, 3NBN, 3V79 |
|
|
| Identifiers |
|---|
| Aliases | RBPJ, AOS3, CBF1, IGKJRB, IGKJRB1, KBF2, RBP-J, RBPJK, RBPSUH, SUH, csl, recombination signal binding protein for immunoglobulin kappa J region, RBP-J kappa, RBP-JK, CBF-1 |
|---|
| External IDs | OMIM: 147183; MGI: 96522; HomoloGene: 7511; GeneCards: RBPJ; OMA:RBPJ - orthologs |
|---|
| Gene location (Human) |
|---|
 | | Chr. | Chromosome 4 (human)[1] |
|---|
| | Band | 4p15.2 | Start | 26,163,455 bp[1] |
|---|
| End | 26,435,131 bp[1] |
|---|
|
| Gene location (Mouse) |
|---|
 | | Chr. | Chromosome 5 (mouse)[2] |
|---|
| | Band | 5 C1|5 29.37 cM | Start | 53,623,494 bp[2] |
|---|
| End | 53,814,704 bp[2] |
|---|
|
| RNA expression pattern |
|---|
| Bgee | | Human | Mouse (ortholog) |
|---|
| Top expressed in | - inferior olivary nucleus
- Achilles tendon
- nipple
- corpus callosum
- dorsal motor nucleus of vagus nerve
- middle temporal gyrus
- synovial joint
- inferior ganglion of vagus nerve
- pericardium
- visceral pleura
|
| | Top expressed in | - vestibular membrane of cochlear duct
- stroma of bone marrow
- ventricular zone
- zygote
- renal corpuscle
- carotid body
- ciliary body
- Paneth cell
- medial ganglionic eminence
- ankle
|
| | More reference expression data |
|
|---|
| BioGPS |  | | More reference expression data |
|
|---|
|
| Gene ontology |
|---|
| Molecular function | - protein N-terminus binding
- protein binding
- DNA strand exchange activity
- chromatin binding
- DNA-binding transcription activator activity, RNA polymerase II-specific
- DNA binding
- transcription factor activity, RNA polymerase II core promoter proximal region sequence-specific binding
- DNA-binding transcription factor activity
- sequence-specific DNA binding
- transcription factor binding
- RNA polymerase II cis-regulatory region sequence-specific DNA binding
- DNA-binding transcription factor activity, RNA polymerase II-specific
| | Cellular component | - nucleolus
- MAML1-RBP-Jkappa- ICN1 complex
- transcription regulator complex
- cytoplasm
- nucleus
- nucleoplasm
- transcription repressor complex
| | Biological process | - artery morphogenesis
- regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II
- neuron differentiation
- epidermal cell fate specification
- positive regulation of cell population proliferation
- club cell differentiation
- somatic stem cell population maintenance
- endocardium development
- cell fate commitment
- DNA recombination
- somitogenesis
- positive regulation of transcription from RNA polymerase II promoter in response to hypoxia
- defense response to bacterium
- regulation of timing of cell differentiation
- regulation of transcription, DNA-templated
- humoral immune response
- keratinocyte differentiation
- hair follicle maturation
- negative regulation of cell population proliferation
- pituitary gland development
- negative regulation of cell differentiation
- Notch signaling involved in heart development
- transcription, DNA-templated
- positive regulation of gene expression
- arterial endothelial cell fate commitment
- myeloid dendritic cell differentiation
- blood vessel remodeling
- secondary heart field specification
- regulation of cell population proliferation
- positive regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II
- transcription initiation from RNA polymerase II promoter
- sebaceous gland development
- positive regulation of canonical Wnt signaling pathway involved in cardiac muscle cell fate commitment
- inflammatory response to antigenic stimulus
- heart development
- auditory receptor cell fate commitment
- B cell differentiation
- regulation of gene expression
- Notch signaling pathway
- dorsal aorta morphogenesis
- atrioventricular canal development
- positive regulation of ephrin receptor signaling pathway
- epithelial to mesenchymal transition involved in endocardial cushion formation
- outflow tract morphogenesis
- cardiac left ventricle morphogenesis
- negative regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II
- labyrinthine layer blood vessel development
- blood vessel lumenization
- endocardium morphogenesis
- ventricular trabecula myocardium morphogenesis
- negative regulation of ossification
- positive regulation of cell proliferation involved in heart morphogenesis
- positive regulation of cardiac muscle cell proliferation
- angiogenesis
- epithelial to mesenchymal transition
- positive regulation of BMP signaling pathway
- positive regulation of ERBB signaling pathway
- blood vessel endothelial cell fate specification
- negative regulation of transcription, DNA-templated
- positive regulation of transcription of Notch receptor target
- positive regulation of Notch signaling pathway
- hemopoiesis
- aortic valve development
- pulmonary valve development
- ventricular septum morphogenesis
- negative regulation of cold-induced thermogenesis
| | Sources:Amigo / QuickGO |
|
| Orthologs |
|---|
| Species | Human | Mouse |
|---|
| Entrez | | |
|---|
| Ensembl | | |
|---|
| UniProt | | |
|---|
| RefSeq (mRNA) | NM_005349
NM_015874
NM_203283
NM_203284
NM_001363577
|
|---|
NM_001374400
NM_001374401
NM_001374402
NM_001374403
NM_001379406
NM_001379407
NM_001379408
NM_001379409 |
| |
|---|
NM_001080927
NM_001080928
NM_001277116
NM_009035
NM_001359152 |
|
|---|
| RefSeq (protein) | NP_005340
NP_056958
NP_976028
NP_976029
NP_001350506
|
|---|
NP_001361329
NP_001361330
NP_001361331
NP_001361332
NP_001366335
NP_001366336
NP_001366337
NP_001366338 |
| |
|---|
NP_001074396
NP_001074397
NP_001264045
NP_033061
NP_001346081 |
|
|---|
| Location (UCSC) | Chr 4: 26.16 – 26.44 Mb | Chr 5: 53.62 – 53.81 Mb |
|---|
| PubMed search | [3] | [4] |
|---|
|
| Wikidata |
| View/Edit Human | View/Edit Mouse |
|

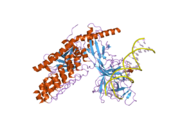 2f8x: Crystal structure of activated Notch, CSL and MAML on HES-1 promoter DNA sequence
2f8x: Crystal structure of activated Notch, CSL and MAML on HES-1 promoter DNA sequence


















