ATBF1
Protein-coding gene in humans
| ZFHX3 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Identifiers | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Aliases | ZFHX3, ATBF1, ATBT, ZNF927, zinc finger homeobox 3 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| External IDs | OMIM: 104155 MGI: 99948 HomoloGene: 21366 GeneCards: ZFHX3 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Wikidata | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Zinc finger homeobox protein 3 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ZFHX3 gene.[5][6][7]
References
- ^ a b c GRCh38: Ensembl release 89: ENSG00000140836 – Ensembl, May 2017
- ^ a b c GRCm38: Ensembl release 89: ENSMUSG00000038872 – Ensembl, May 2017
- ^ "Human PubMed Reference:". National Center for Biotechnology Information, U.S. National Library of Medicine.
- ^ "Mouse PubMed Reference:". National Center for Biotechnology Information, U.S. National Library of Medicine.
- ^ Morinaga T, Yasuda H, Hashimoto T, Higashio K, Tamaoki T (Dec 1991). "A human alpha-fetoprotein enhancer-binding protein, ATBF1, contains four homeodomains and seventeen zinc fingers". Mol Cell Biol. 11 (12): 6041–9. doi:10.1128/MCB.11.12.6041. PMC 361769. PMID 1719379.
- ^ Miura Y, Tam T, Ido A, Morinaga T, Miki T, Hashimoto T, Tamaoki T (Dec 1995). "Cloning and characterization of an ATBF1 isoform that expresses in a neuronal differentiation-dependent manner". J Biol Chem. 270 (45): 26840–8. doi:10.1074/jbc.270.45.26840. PMID 7592926.
- ^ "Entrez Gene: ATBF1 AT-binding transcription factor 1".
Further reading
- Yamada K, Miura Y, Scheidl T, et al. (1996). "Assignment of the human ATBF1 transcription factor gene to chromosome 16q22.3-q23.1". Genomics. 29 (2): 552–3. doi:10.1006/geno.1995.9967. PMID 8666409.
- Bedford MT, Chan DC, Leder P (1997). "FBP WW domains and the Abl SH3 domain bind to a specific class of proline-rich ligands". EMBO J. 16 (9): 2376–83. doi:10.1093/emboj/16.9.2376. PMC 1169838. PMID 9171351.
- Kaspar P, Dvoráková M, Králová J, et al. (1999). "Myb-interacting protein, ATBF1, represses transcriptional activity of Myb oncoprotein". J. Biol. Chem. 274 (20): 14422–8. doi:10.1074/jbc.274.20.14422. PMID 10318867.
- Loftus BJ, Kim UJ, Sneddon VP, et al. (1999). "Genome duplications and other features in 12 Mb of DNA sequence from human chromosome 16p and 16q". Genomics. 60 (3): 295–308. doi:10.1006/geno.1999.5927. PMID 10493829.
- Kaushik N, Malaspina A, de Belleroche J (2000). "Characterization of trinucleotide- and tandem repeat-containing transcripts obtained from human spinal cord cDNA library by high-density filter hybridization". DNA Cell Biol. 19 (5): 265–73. doi:10.1089/10445490050021177. PMID 10855793.
- Strausberg RL, Feingold EA, Grouse LH, et al. (2003). "Generation and initial analysis of more than 15,000 full-length human and mouse cDNA sequences". Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 99 (26): 16899–903. Bibcode:2002PNAS...9916899M. doi:10.1073/pnas.242603899. PMC 139241. PMID 12477932.
- Iida M, Imura J, Furuichi T, et al. (2004). "Alteration of the AT motif binding factor-1 expression in alpha-fetoprotein producing gastric cancer: is it an event for differentiation and proliferation of the tumors?". Oncol. Rep. 11 (1): 3–7. doi:10.3892/or.11.1.3. PMID 14654895.
- Nojiri S, Joh T, Miura Y, et al. (2004). "ATBF1 enhances the suppression of STAT3 signaling by interaction with PIAS3". Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 314 (1): 97–103. doi:10.1016/j.bbrc.2003.12.054. PMID 14715251.
- Martin J, Han C, Gordon LA, et al. (2005). "The sequence and analysis of duplication-rich human chromosome 16". Nature. 432 (7020): 988–94. Bibcode:2004Natur.432..988M. doi:10.1038/nature03187. PMID 15616553.
- Zhang Z, Yamashita H, Toyama T, et al. (2005). "ATBF1-a messenger RNA expression is correlated with better prognosis in breast cancer". Clin. Cancer Res. 11 (1): 193–8. doi:10.1158/1078-0432.193.11.1. PMID 15671546.
- Sun X, Frierson HF, Chen C, et al. (2005). "Frequent somatic mutations of the transcription factor ATBF1 in human prostate cancer". Nat. Genet. 37 (4): 407–12. doi:10.1038/ng1528. PMID 15750593. S2CID 19458711.
- Rual JF, Venkatesan K, Hao T, et al. (2005). "Towards a proteome-scale map of the human protein-protein interaction network". Nature. 437 (7062): 1173–8. Bibcode:2005Natur.437.1173R. doi:10.1038/nature04209. PMID 16189514. S2CID 4427026.
- Xu J, Sauvageot J, Ewing CM, et al. (2006). "Germline ATBF1 mutations and prostate cancer risk". Prostate. 66 (10): 1082–5. doi:10.1002/pros.20430. PMID 16637072. S2CID 21238472.
- Sun X, Zhou Y, Otto KB, et al. (2007). "Infrequent mutation of ATBF1 in human breast cancer". J. Cancer Res. Clin. Oncol. 133 (2): 103–5. doi:10.1007/s00432-006-0148-y. PMID 16932943. S2CID 12378418.
- Olsen JV, Blagoev B, Gnad F, et al. (2006). "Global, in vivo, and site-specific phosphorylation dynamics in signaling networks". Cell. 127 (3): 635–48. doi:10.1016/j.cell.2006.09.026. PMID 17081983. S2CID 7827573.
- Mori Y, Kataoka H, Miura Y, et al. (2007). "Subcellular localization of ATBF1 regulates MUC5AC transcription in gastric cancer". Int. J. Cancer. 121 (2): 241–7. doi:10.1002/ijc.22654. PMID 17330845. S2CID 37176312.
- Cho YG, Song JH, Kim CJ, et al. (2007). "Genetic alterations of the ATBF1 gene in gastric cancer". Clin. Cancer Res. 13 (15 Pt 1): 4355–9. doi:10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-07-0619. PMID 17671116.
External links
- ATBF1+protein,+human at the U.S. National Library of Medicine Medical Subject Headings (MeSH)
- Human ZFHX3 genome location and ZFHX3 gene details page in the UCSC Genome Browser.
- v
- t
- e
PDB gallery
-
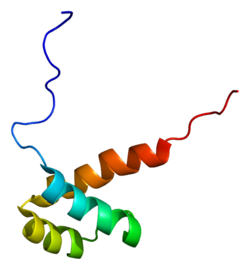
 2da1: Solution structure of the first homeobox domain of AT-binding transcription factor 1 (ATBF1)
2da1: Solution structure of the first homeobox domain of AT-binding transcription factor 1 (ATBF1) -
 2da2: Solution structure of the second homeobox domain of AT-binding transcription factor 1 (ATBF1)
2da2: Solution structure of the second homeobox domain of AT-binding transcription factor 1 (ATBF1) -
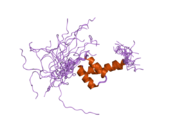 2da3: Solution structure of the third homeobox domain of AT-binding transcription factor 1 (ATBF1)
2da3: Solution structure of the third homeobox domain of AT-binding transcription factor 1 (ATBF1)
 | This article on a gene on human chromosome 16 is a stub. You can help Wikipedia by expanding it. |
- v
- t
- e