Gabelsberger shorthand
| Gabelsberger shorthand | |
|---|---|
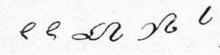 | |
| Script type | light-line script mixed abugida Shorthand |
| Creator | Franz Xaver Gabelsberger |
| Created | ≈1817 |
| Published | 1834 |
Time period | 1834-1924 |
| Languages | German |
| Related scripts | |
Child systems | German Unified Shorthand (Deutsche Einheitskurzschrift) Bezenšek Shorthand Gabelsberger-Noë Shorthand |
| This article contains phonetic transcriptions in the International Phonetic Alphabet (IPA). For an introductory guide on IPA symbols, see Help:IPA. For the distinction between [ ], / / and ⟨ ⟩, see IPA § Brackets and transcription delimiters. | |

Gabelsberger shorthand, named for its creator, is a form of shorthand previously common in Germany and Austria. Created c. 1817 by Franz Xaver Gabelsberger, it was first fully described in the 1834 textbook Anleitung zur deutschen Redezeichenkunst oder Stenographie and became rapidly used.
Gabelsberger shorthand has a full alphabet with signs for both consonants and vowels. The consonant signs were made by simplifying the features of cursive Latin letters. The vowel signs are used mainly when a vowel stands at the beginning or the end of a word. Vowels in the middle of words are represented symbolically, mainly by varying the position and the impact of the following consonant signs. Contrary to the practice in many English shorthand systems (e.g. Pitman Shorthand), vowels are never entirely omitted.
Most German shorthand systems published after 1834 are ultimately based on Gabelsberger's system. Modern German shorthand, Deutsche Einheitskurzschrift, retains most of the consonant signs of Gabelsberger's alphabet but has a modified system of vowel representation.
Gabelsberger shorthand was adopted into many languages and was particularly successful in Scandinavia, the Slavic countries, and Italy. A host of shorthand systems has since appeared that build on the graphic principles laid down by Gabelsberger.
External links
- "List of Gabelsberger glyphs". Retrieved 2017-04-06.
- Anleitung zur deutschen Redezeichenkunst oder Stenographie at WorldCat.
 | This writing system–related article is a stub. You can help Wikipedia by expanding it. |
- v
- t
- e
  | This German history article is a stub. You can help Wikipedia by expanding it. |
- v
- t
- e
  | This Austrian history article is a stub. You can help Wikipedia by expanding it. |
- v
- t
- e









