EA-3148
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
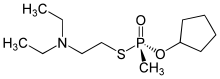
| Preferred IUPAC name O-Cyclopentyl S-[2-(diethylamino)ethyl] methylphosphonothioate | |
| Identifiers | |
CAS Number |
|
3D model (JSmol) |
|
| ChemSpider |
|
PubChem CID |
|
| UNII |
|
InChI
| |
| |
| Properties | |
Chemical formula | C12H26NO2PS |
| Molar mass | 279.378 g/mol |
| Density | 1.05 g/cm3 |
| Boiling point | 111.11 °C (232.00 °F; 384.26 K) |
| Hazards | |
| Occupational safety and health (OHS/OSH): | |
Main hazards | Extremely Toxic |
| NFPA 704 (fire diamond) |  4 1 1 |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).  N verify (what is N verify (what is  Y Y N ?) N ?) Infobox references | |
| Part of a series on | ||||||
| Chemical agents | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Lethal agents | ||||||
| Blood
| ||||||
| Blister
| ||||||
| ||||||
| ||||||
| Incapacitating agents | ||||||
| ||||||
|
EA-3148 (Substance 100A) is a "V-series" nerve agent related to the better-known compounds VX and VR.[1] It was studied by both the US and Soviet chemical weapons programmes during the Cold War, and is notable as the only V-series organophosphate nerve agent specifically identified in public domain sources as having a higher absolute potency as an acetylcholinesterase inhibitor than VX (around 50% more potent by weight).[2] However, both the US and Soviet investigations of the compound concluded that despite its high potency, the physicochemical properties of the substance made it unsuitable for weaponisation, and further research was not conducted.[3]
The chemical structure of EA-3148 falls within the scope of compounds designated "Toxic chemicals" under Schedule 1 of the Chemical Weapons Convention and so it is illegal throughout the world under international law and may only be used for certain types of scientific and medical research.
Effects
A healthy American male soldier was given EA-3148, 1.15 µg/kg i.v.. Erythrocyte AChE values dropped precipitously to 22% of normal within 15 min of dosing and to 0% at 48 h; the value recovered to 88% of normal at 72 days post-exposure. Signs of toxicity were evident within 5-8 min of treatment in two comparably dosed subjects who felt dizzy, weak, tired, sweaty, and had hands and feet that were moist. Within 2 h post-exposure, these subjects reportedly were resting, eating, and feeling fine.
A U.S. Army report summarizing experience with EA-3148 noted anorexia, fatigue, poor sleep, unusual dreams, dizziness, euphoria, blurred vision, increased salivation, restlessness; decrements in a test of numerical facility in four individuals and exaggeration of a schizoid personality in one male soldier.[4]
References
- ^ Ellison, D. H. (2008). Handbook of Chemical and Biological Warfare Agents (2nd ed.). p. 28. ISBN 978-0-8493-1434-6.
- ^ Commission on Life Sciences (1982). Possible Long-Term Health Effects of Short-Term Exposure to Chemical Agents. Vol. 1. The National Academies Press. pp. 7, 22, 29, E3.
- ^ Mirzayanov, V. S. (2009). State Secrets. An Insider's Chronicle of the Russian Chemical Weapons Program. pp. 127–128. ISBN 978-1-4327-2566-2.
- ^ Barry W. Wilson, Ph.D.. Low-Level Sarion Neurotoxicity and its Modulation by Pyridostigmine. University of California Davis, California.











