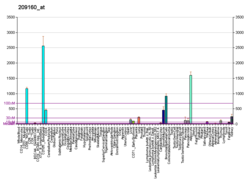
AKR1C3
| AKR1C3 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Identifiers | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Aliases | AKR1C3, DD3, DDX, HA1753, HAKRB, HAKRe, HSD17B5, PGFS, hluPGFS, aldo-keto reductase family 1, member C3, aldo-keto reductase family 1 member C3 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| External IDs | OMIM: 603966; MGI: 2145420; HomoloGene: 128661; GeneCards: AKR1C3; OMA:AKR1C3 - orthologs | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| EC number | 1.3.1.20 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Wikidata | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Aldo-keto reductase family 1 member C3 (AKR1C3), also known as 17β-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase type 5 (17β-HSD5, HSD17B5) or 3α-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase type 2 (3α-HSD2)[5][6][7] is a steroidogenic enzyme that in humans is encoded by the AKR1C3 gene.[8][9][10]
Function
This gene encodes a member of the aldo/keto reductase superfamily, which consists of more than 40 known enzymes and proteins. These enzymes catalyze the conversion of aldehydes and ketones to their corresponding alcohols by utilizing NADH and/or NADPH as cofactors. The enzymes display overlapping but distinct substrate specificity. This enzyme catalyzes the reduction of prostaglandin D2, prostaglandin H2, and phenanthrenequinone, and the oxidation of prostaglandin F2α to prostaglandin D2.[10] It is also capable of metabolizing estrogen and progesterone.[11]
AKR1C3 may play an important role in the development of allergic diseases such as asthma, and may also have a role in controlling cell growth and/or differentiation. This gene shares high sequence identity with three other gene members and is clustered with those three genes at chromosome 10p15-p14.[10]
Pathology
AKR1C3 is overexpressed in prostate cancer (PCa) and is associated with the development of castration-resistant prostate cancer (CRPC). In addition, AKR1C3 overexpression may serve as a promising biomarker for prostate cancer progression.[12]
Isozymes of aldo-keto reductase family 1 member C
| HGNC Gene Symbol | Enzyme Name Aliases[13] |
|---|---|
| AKR1C1 | aldo-keto reductase family 1 member C1; 20α-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase |
| AKR1C2 | aldo-keto reductase family 1 member C2; 3α-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase type 3 |
| AKR1C3 | aldo-keto reductase family 1 member C3; 3α-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase type 2; 17β-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase type 5; HSD17B5 |
| AKR1C4 | aldo-keto reductase family 1 member C4; 3α-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase type 1 |
See also
References
- ^ a b c GRCh38: Ensembl release 89: ENSG00000196139 – Ensembl, May 2017
- ^ a b c GRCm38: Ensembl release 89: ENSMUSG00000021214 – Ensembl, May 2017
- ^ "Human PubMed Reference:". National Center for Biotechnology Information, U.S. National Library of Medicine.
- ^ "Mouse PubMed Reference:". National Center for Biotechnology Information, U.S. National Library of Medicine.
- ^ Zhang B, Zhu DW, Hu XJ, Zhou M, Shang P, Lin SX (May 2014). "Human 3-alpha hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase type 3 (3α-HSD3): The V54L mutation restricting the steroid alternative binding and enhancing the 20α-HSD activity". The Journal of Steroid Biochemistry and Molecular Biology. 141: 135–143. doi:10.1016/j.jsbmb.2014.01.003. PMID 24434280.
- ^ Li T, Zhang W, Lin SX (February 2020). "Steroid enzyme and receptor expression and regulations in breast tumor samples – A statistical evaluation of public data". The Journal of Steroid Biochemistry and Molecular Biology. 196: 105494. doi:10.1016/j.jsbmb.2019.105494. PMID 31610224.
- ^ Masiutin MM, Yadav MK (3 April 2023). "Alternative androgen pathways" (PDF). WikiJournal of Medicine. 10: 29. doi:10.15347/WJM/2023.003. S2CID 257943362.
 This article incorporates text from this source, which is available under the CC BY 4.0 license.
This article incorporates text from this source, which is available under the CC BY 4.0 license. - ^ Khanna M, Qin KN, Wang RW, Cheng KC (August 1995). "Substrate Specificity, Gene Structure, and Tissue-specific Distribution of Multiple Human 3α-Hydroxysteroid Dehydrogenases". Journal of Biological Chemistry. 270 (34): 20162–20168. doi:10.1074/jbc.270.34.20162. PMID 7650035.
- ^ Matsuura K, Shiraishi H, Hara A, Sato K, Deyashiki Y, Ninomiya M, Sakai S (November 1998). "Identification of a Principal mRNA Species for Human 3 -Hydroxysteroid Dehydrogenase Isoform (AKR1C3) That Exhibits High Prostaglandin D2 11-Ketoreductase Activity". Journal of Biochemistry. 124 (5): 940–946. doi:10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a022211. PMID 9792917.
- ^ a b c EntrezGene 8644 AKR1C3 aldo-keto reductase family 1 member C3 [ Homo sapiens (human) ]
- ^ Theisen JG, Sundaram V, Filchak MS, Chorich LP, Sullivan ME, Knight J, Kim HG, Layman LC (27 December 2019). "The Use of Whole Exome Sequencing in a Cohort of Transgender Individuals to Identify Rare Genetic Variants". Scientific Reports. 9 (1). Table 4. Bibcode:2019NatSR...920099T. doi:10.1038/s41598-019-53500-y. PMC 6934803. PMID 31882810.
- ^ Tian Y, Zhao L, Zhang H, Liu X, Zhao L, Zhao X, Li Y, Li J (December 2014). "AKR1C3 overexpression may serve as a promising biomarker for prostate cancer progression". Diagnostic Pathology. 9 (1): 42. doi:10.1186/1746-1596-9-42. PMC 3939640. PMID 24571686.
- ^ Dufort I, Labrie F, Luu-The V (February 2001). "Human types 1 and 3 3 alpha-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenases: differential lability and tissue distribution". J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 86 (2): 841–6. doi:10.1210/jcem.86.2.7216. PMID 11158055.
human types 1 and 3 3α-HSD, 20α-HSD, and type 5 17β-HSD were named AKR1C4, AKR1C2, AKR1C1, and AKR1C3, respectively
External links
- Human AKR1C3 genome location and AKR1C3 gene details page in the UCSC Genome Browser.
Further reading
- Lin SX, Shi R, Qiu W, Azzi A, Zhu DW, Dabbagh HA, Zhou M (Mar 2006). "Structural basis of the multispecificity demonstrated by 17beta-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase types 1 and 5". Molecular and Cellular Endocrinology. 248 (1–2): 38–46. doi:10.1016/j.mce.2005.11.035. PMID 16480815. S2CID 19087697.
- Khanna M, Qin KN, Cheng KC (Jun 1995). "Distribution of 3 alpha-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase in rat brain and molecular cloning of multiple cDNAs encoding structurally related proteins in humans". The Journal of Steroid Biochemistry and Molecular Biology. 53 (1–6): 41–6. doi:10.1016/0960-0760(95)00019-V. PMID 7626489. S2CID 11316547.
- Nagase T, Miyajima N, Tanaka A, Sazuka T, Seki N, Sato S, Tabata S, Ishikawa K, Kawarabayasi Y, Kotani H (1995). "Prediction of the coding sequences of unidentified human genes. III. The coding sequences of 40 new genes (KIAA0081-KIAA0120) deduced by analysis of cDNA clones from human cell line KG-1". DNA Research. 2 (1): 37–43. doi:10.1093/dnares/2.1.37. PMID 7788527.
- Khanna M, Qin KN, Klisak I, Belkin S, Sparkes RS, Cheng KC (Jan 1995). "Localization of multiple human dihydrodiol dehydrogenase (DDH1 and DDH2) and chlordecone reductase (CHDR) genes in chromosome 10 by the polymerase chain reaction and fluorescence in situ hybridization". Genomics. 25 (2): 588–90. doi:10.1016/0888-7543(95)80066-U. PMID 7789999.
- Qin KN, New MI, Cheng KC (Dec 1993). "Molecular cloning of multiple cDNAs encoding human enzymes structurally related to 3 alpha-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase". The Journal of Steroid Biochemistry and Molecular Biology. 46 (6): 673–9. doi:10.1016/0960-0760(93)90308-J. PMID 8274401. S2CID 36210133.
- Bennett MJ, Schlegel BP, Jez JM, Penning TM, Lewis M (Aug 1996). "Structure of 3 alpha-hydroxysteroid/dihydrodiol dehydrogenase complexed with NADP+". Biochemistry. 35 (33): 10702–11. doi:10.1021/bi9604688. PMID 8718859.
- Lin HK, Jez JM, Schlegel BP, Peehl DM, Pachter JA, Penning TM (Dec 1997). "Expression and characterization of recombinant type 2 3 alpha-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase (HSD) from human prostate: demonstration of bifunctional 3 alpha/17 beta-HSD activity and cellular distribution". Molecular Endocrinology. 11 (13): 1971–84. doi:10.1210/mend.11.13.0026. PMID 9415401.
- Mills KI, Gilkes AF, Sweeney M, Choudhry MA, Woodgate LJ, Bunce CM, Brown G, Burnett AK (Nov 1998). "Identification of a retinoic acid responsive aldoketoreductase expressed in HL60 leukaemic cells". FEBS Letters. 440 (1–2): 158–62. Bibcode:1998FEBSL.440..158M. doi:10.1016/S0014-5793(98)01435-5. PMID 9862446. S2CID 21355070.
- Dufort I, Rheault P, Huang XF, Soucy P, Luu-The V (Feb 1999). "Characteristics of a highly labile human type 5 17beta-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase". Endocrinology. 140 (2): 568–74. doi:10.1210/endo.140.2.6531. PMID 9927279.
- Rheault P, Dufort I, Soucy P, Luu-The V (1999). "Assignment of HSD17B5 encoding type 5 17 beta-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase to human chromosome bands 10p15-->p14 and mouse chromosome 13 region A2 by in situ hybridization: identification of a new syntenic relationship". Cytogenetics and Cell Genetics. 84 (3–4): 241–2. doi:10.1159/000015267. PMID 10393440. S2CID 5792836.
- Griffin LD, Mellon SH (Nov 1999). "Selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors directly alter activity of neurosteroidogenic enzymes". Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America. 96 (23): 13512–7. Bibcode:1999PNAS...9613512G. doi:10.1073/pnas.96.23.13512. PMC 23979. PMID 10557352.
- Suzuki-Yamamoto T, Nishizawa M, Fukui M, Okuda-Ashitaka E, Nakajima T, Ito S, Watanabe K (Dec 1999). "cDNA cloning, expression and characterization of human prostaglandin F synthase". FEBS Letters. 462 (3): 335–40. doi:10.1016/S0014-5793(99)01551-3. PMID 10622721. S2CID 19812463.
- Nishizawa M, Nakajima T, Yasuda K, Kanzaki H, Sasaguri Y, Watanabe K, Ito S (Feb 2000). "Close kinship of human 20alpha-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase gene with three aldo-keto reductase genes". Genes to Cells. 5 (2): 111–25. doi:10.1046/j.1365-2443.2000.00310.x. PMID 10672042. S2CID 25136637.
- Penning TM, Burczynski ME, Jez JM, Hung CF, Lin HK, Ma H, Moore M, Palackal N, Ratnam K (Oct 2000). "Human 3alpha-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase isoforms (AKR1C1-AKR1C4) of the aldo-keto reductase superfamily: functional plasticity and tissue distribution reveals roles in the inactivation and formation of male and female sex hormones". The Biochemical Journal. 351 (Pt 1): 67–77. doi:10.1042/bj3510067. PMC 1221336. PMID 10998348.
- Hartley JL, Temple GF, Brasch MA (Nov 2000). "DNA cloning using in vitro site-specific recombination". Genome Research. 10 (11): 1788–95. doi:10.1101/gr.143000. PMC 310948. PMID 11076863.
- Penning TM, Burczynski ME, Jez JM, Lin HK, Ma H, Moore M, Ratnam K, Palackal N (Jan 2001). "Structure-function aspects and inhibitor design of type 5 17beta-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase (AKR1C3)". Molecular and Cellular Endocrinology. 171 (1–2): 137–49. doi:10.1016/S0303-7207(00)00426-3. PMID 11165022. S2CID 11599113.
- Simpson JC, Wellenreuther R, Poustka A, Pepperkok R, Wiemann S (Sep 2000). "Systematic subcellular localization of novel proteins identified by large-scale cDNA sequencing". EMBO Reports. 1 (3): 287–92. doi:10.1093/embo-reports/kvd058. PMC 1083732. PMID 11256614.
- v
- t
- e
-
 1ry0: Structure of prostaglandin F synthase with prostaglandin D2
1ry0: Structure of prostaglandin F synthase with prostaglandin D2 -
 1ry8: Prostaglandin F synthase complexed with NADPH and rutin
1ry8: Prostaglandin F synthase complexed with NADPH and rutin -
 1s1p: Crystal structures of prostaglandin D2 11-ketoreductase (AKR1C3) in complex with the non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs flufenamic acid and indomethacin
1s1p: Crystal structures of prostaglandin D2 11-ketoreductase (AKR1C3) in complex with the non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs flufenamic acid and indomethacin -
 1s1r: Crystal structures of prostaglandin D2 11-ketoreductase (AKR1C3) in complex with the non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs flufenamic acid and indomethacin
1s1r: Crystal structures of prostaglandin D2 11-ketoreductase (AKR1C3) in complex with the non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs flufenamic acid and indomethacin -
 1s2a: Crystal structures of prostaglandin D2 11-ketoreductase in complex with the non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs flufenamic acid and indomethacin
1s2a: Crystal structures of prostaglandin D2 11-ketoreductase in complex with the non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs flufenamic acid and indomethacin -
 1s2c: Crystal structures of prostaglandin D2 11-ketoreductase in complex with the non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs flufenamic acid and indomethacin
1s2c: Crystal structures of prostaglandin D2 11-ketoreductase in complex with the non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs flufenamic acid and indomethacin -
 1xf0: Crystal structure of human 17beta-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase type 5 (AKR1C3) complexed with delta4-androstene-3,17-dione and NADP
1xf0: Crystal structure of human 17beta-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase type 5 (AKR1C3) complexed with delta4-androstene-3,17-dione and NADP -
 1zq5: Crystal structure of human androgenic 17beta-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase type 5 in complexed with a potent inhibitor EM1404
1zq5: Crystal structure of human androgenic 17beta-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase type 5 in complexed with a potent inhibitor EM1404 -
 2f38: Crystal structure of prostaglandin F synathase containing bimatoprost
2f38: Crystal structure of prostaglandin F synathase containing bimatoprost -
 2fgb: Crystal structure of human 17bet a-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase type 5 in complexes with PEG and NADP
2fgb: Crystal structure of human 17bet a-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase type 5 in complexes with PEG and NADP
 | This article on a gene on human chromosome 10 is a stub. You can help Wikipedia by expanding it. |
- v
- t
- e