Sodium diacetate
 Sodium diacetate | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name Sodium diacetate | |
| Other names Sodium diacetate (anhydrous); Sodium hydrogen acetate; Sodium acid acetate | |
| Identifiers | |
CAS Number |
|
3D model (JSmol) |
|
| ChemSpider |
|
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.004.378 |
| MeSH | diacetate sodium diacetate |
PubChem CID |
|
| UNII |
|
CompTox Dashboard (EPA) |
|
InChI
| |
| |
| Properties | |
Chemical formula | C4H7NaO4 |
| Molar mass | 142.086 g·mol−1 |
| Appearance | White powder |
| Odor | Acetic acid (vinegar) odor |
Solubility in water | 1 g/mL |
| Solubility in alcohol | Slightly |
| Solubility in ether | Insoluble |
| Hazards | |
| Occupational safety and health (OHS/OSH): | |
Inhalation hazards | Irritant[1] |
Eye hazards | Irritant[1] |
| GHS labelling:[1] | |
Pictograms |   |
| Danger | |
| H318, H319 | |
| P264, P280, P305+P351+P338, P310, P337+P313 | |
| Flash point | >150 °C (302 °F)[1] |
| Lethal dose or concentration (LD, LC): | |
LD50 (median dose) | >2,000 mg/kg (rat, dermal), 5,600 mg/kg (rat, oral) |
| Safety data sheet (SDS) | PubChem sodium diacetate LCSS |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). Infobox references | |
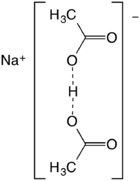
Sodium diacetate is a compound with formula NaH(C
2H
3O
2)
2. It is a salt of acetic acid. It is a colorless solid that is used in seasonings and as an antimicrobial agent.
Preparation and structure
The salt forms upon half-neutralization of acetic acid followed by evaporation of the solution. It can be viewed as the result of homoassociation, an effect that enhances the acidity of acetic acid in concentrated solution:
- 2 CH3CO2H + NaOH → Na+[(CH3CO2)2H]− + H2O
Also described as the sodium acid salt of acetic acid, it is best described as the sodium salt of the hydrogen-bonded anion (CH3CO2)2H−. The O···O distance is about 2.47 angstrom.[2] The species has no significant existence in solution but forms stable crystals.
Applications
As a food additive,[3] it has E number E262 and is used to impart a salt and vinegar flavor.
See also
References
- ^ a b c d PubChem. "Sodium diacetate". PubChem. Retrieved 2019-10-24.
- ^ Barrow, Michael J.; Currie, Murdoch; Muir, Kenneth W.; Speakman, J. Clare; White, David N, J. "Crystal structures of some acid salts of monobasic acids. XVII. Structure of sodium hydrogen diacetate, redetermined by neutron diffraction" Journal of the Chemical Society, Perkin Transactions 2: Physical Organic Chemistry 1975, pp. 15-18. doi:10.1039/P29750000015
- ^ Peter J. Taormina "Implications of Salt and Sodium Reduction on Microbial Food Safety" in Critical Reviews in Food Science and Nutrition, 2010, vol. 50, 209-227. doi:10.1080/10408391003626207
- v
- t
- e
| AcOH | He | ||||||||||||||||||||
| LiOAc | Be(OAc)2 Be4O(OAc)6 | B(OAc)3 B2O(OAc)4 | AcOAc ROAc | NH4OAc | AcOOH | FAc FOAc | Ne | ||||||||||||||
| NaOAc NaH(OAc)2 | Mg(OAc)2 | Al(OAc)3 ALSOL Al(OAc)2OH Al(OH)2OAc Al2SO4(OAc)4 | Si | P | S | ClAc ClOAc | Ar | ||||||||||||||
| KOAc | Ca(OAc)2 | Sc(OAc)3 | Ti(OAc)4 | VO(OAc)3 | Cr(OAc)2 Cr(OAc)3 | Mn(OAc)2 Mn(OAc)3 | Fe(OAc)2 Fe(OAc)3 | Co(OAc)2 | Ni(OAc)2 | CuOAc Cu(OAc)2 | Zn(OAc)2 | Ga(OAc)3 | Ge | As(OAc)3 | Se | BrAc BrOAc | Kr | ||||
| RbOAc | Sr(OAc)2 | Y(OAc)3 | Zr(OAc)4 | Nb | Mo(OAc)2 | Tc | Ru2(OAc)4Cl Ru(OAc)3 | Rh2(OAc)4 | Pd(OAc)2 | AgOAc | Cd(OAc)2 | In(OAc)3 | Sn(OAc)2 Sn(OAc)4 | Sb(OAc)3 | Te | IAc IOAc I(OAc)3 | Xe | ||||
| CsOAc | Ba(OAc)2 | * | Lu(OAc)3 | Hf | Ta | W | Re | Os | Ir | Pt(OAc)2 | Au(OAc)3 | Hg2(OAc)2 Hg(OAc)2 | TlOAc Tl(OAc)3 | Pb(OAc)2 Pb(OAc)4 | Bi(OAc)3 | Po | At | Rn | |||
| Fr | Ra | ** | Lr | Rf | Db | Sg | Bh | Hs | Mt | Ds | Rg | Cn | Nh | Fl | Mc | Lv | Ts | Og | |||
| * | La(OAc)3 | Ce(OAc)3 | Pr(OAc)3 | Nd(OAc)3 | Pm | Sm(OAc)3 | Eu(OAc)3 | Gd(OAc)3 | Tb(OAc)3 | Dy(OAc)3 | Ho(OAc)3 | Er(OAc)3 | Tm(OAc)3 | Yb(OAc)3 | |||||||
| ** | Ac(OAc)3 | Th(OAc)4 | Pa | UO2(OAc)2 | Np | Pu | Am | Cm | Bk | Cf | Es | Fm | Md | No | |||||||











