Phenolic acid
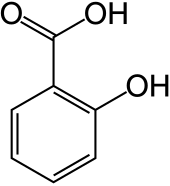
Phenolic acids or phenolcarboxylic acids are phenolic compounds and types of aromatic acid compounds. Included in that class are substances containing a phenolic ring and an organic carboxylic acid function (C6-C1 skeleton). Two important naturally occurring types of phenolic acids are hydroxybenzoic acids and hydroxycinnamic acids, which are derived from non-phenolic molecules of benzoic and cinnamic acid, respectively.[1]
Occurrences
Phenolic acids can be found in many plant species. Their content in dried fruits can be high.
Natural phenols in horse grams (Macrotyloma uniflorum) are mostly phenolic acids, namely 3,4-dihydroxy benzoic, p-hydroxy benzoic, vanillic, caffeic, p-coumaric, ferulic, syringic, and sinapinic acids.[citation needed]
Phenolic acids can be found in several mushroom-forming species of basidiomycetes.[2] It is also a part of the humic substances, which are the major organic constituents of soil humus.
Many phenolic acids can be found in human urine.[3]
Chemistry
Immobilized Candida antarctica lipase can be used to catalyze the direct acetylation of flavonoids with phenolic acids.[4]
See also
References
- ^ Heleno, Sandrina A.; Martins, Anabela; Queiroz, Maria João R. P.; Ferreira, Isabel C. F. R. (2015-04-15). "Bioactivity of phenolic acids: metabolites versus parent compounds: a review" (PDF). Food Chemistry. 173: 501–513. doi:10.1016/j.foodchem.2014.10.057. hdl:1822/39808. ISSN 0308-8146. PMID 25466052.
- ^ Barros, L.; Dueñas, M.; Ferreira, I. C.; Baptista, P.; Santos-Buelga, C. (June 2009). "Phenolic acids determination by HPLC–DAD–ESI/MS in sixteen different Portuguese wild mushrooms species". Food and Chemical Toxicology. 47 (6): 1076–1079. doi:10.1016/j.fct.2009.01.039. PMID 19425182.
- ^ Armstrong, M. D.; Shaw, K. N.; Wall, P. E. (January 1, 1956). "The phenolic acids of human urine. Paper chromatography of phenolic acids" (PDF). The Journal of Biological Chemistry. 218 (1): 293–303. PMID 13278337.
- ^ Stevenson, David E.; Wibisono, Reginald; Jensen, Dwayne J.; Stanley, Roger A.; Cooney, Janine M. (3 October 2006). "Direct acylation of flavonoid glycosides with phenolic acids catalysed by Candida antarctica lipase B (Novozym 435®)". Enzyme and Microbial Technology. 39 (6): 1236–41. doi:10.1016/j.enzmictec.2006.03.006.












