Marine biodiversity of South Africa


The Marine biodiversity of South Africa is the variety of living organisms that live in the seas off the coast of South Africa. It includes genetic, species and ecosystems biodiversity in a range of habitats spread over a range of ecologically varied regions, influenced by the geomorphology of the seabed and circulation of major and local water masses, which distribute both living organisms and nutrients in complex and time-variable patterns.
South Africa has a wide range of marine diversity with coastline in three oceans, two major current systems, major ocean frontal systems and benthic topography extending to a maximum depth of 5 700 m. There are 179 defined marine ecosystem types, 150 of them around South Africa and 29 around the sub-Antarctic territory of the Prince Edward Islands.[1]
History
Research on biodiversity of South African waters started in the colonial period from the late 18th century to the late 19th century, with shipboard survey and collection expeditions, like the Challenger, Deutsche Tiefsee and Discovery expeditions. From the early 20th century to the 1970s a group of local marine taxonomists such as J.D.F. Gilchrist and K.H. Barnard, described most of the common fauna on a morphological basis, and after 1970 marine research shifted to ecological aspects and taxonomy was largely neglected. This has left the region with a shortage of taxonomic expertise in comparison with most of the developed world.[2]: 21
The SeaKeys project was started in 2014 to help develop foundational marine biodiversity knowledge by addressing some of the more significant gaps. The project had some success in collating species checklists and records, and national inventories covering over 9700 species in various groups were compiled. Data sets were digitised, distribution data updated for fish and benthic invertebrates, and a guide to offshore marine invertebrates was published. This project highlighted the deficit in taxonomic skills, as it became apparent that most of the guides and lists had not changed much since the 1970s. [2]: 22
National Biodiversity Assessments
The National Biodiversity Assessment (NBA) is recurring project by the South African National Biodiversity Institute in collaboration with the Department of Environmental Affairs and several other organisations to assess the state of South Africa's biodiversity over time as an input for policy and decision making where the environment may be affected. The NBA looks into genetic, species and ecosystems biodiversity for terrestrial, freshwater, estuarine and marine environments. Each assessment cycle takes approximately five years, and both generates new knowledge and analyses existing knowledge.[3] NBA reports are named for the year of the data, and are usually published in the following year. They have been published for 2004,[4] 2011,[5] and 2018,[2] and include reports, data, and supplementary documents.[6]
Physical oceanography
Physical oceanography is the sub-domain of oceanography which focuses on the study of physical conditions and processes within the ocean, including the physical properties and circulation of ocean waters. These matters influence the biodiversity by providing the setting in which the ecology and biodiversity evolve.
The physical setting for the biodiversity of the South African coastal and offshore waters is mainly temperate continental shelf, slope and abyss in the South Atlantic and South-west Indian Oceans off the southern part of the continent of Africa. The geomorphology of this region has local effects on the ocean circulation, particularly effects on ocean currents and upwellings, which in turn affect the distribution of organisms and the environment in which they live.
Continental shelf
The continental shelf of southern Africa varies considerably in width along the coast, and the shelf edge also varies in depth. To the north-east the shelf is narrow to very narrow, with a relatively shallow break, but it is much wider over the Agulhas Bank off the southern tip of the continent. This gradual increase in width affects the path of the powerful Agulhas Current, pushing it further offshore towards the Southern Ocean.
Ocean currents


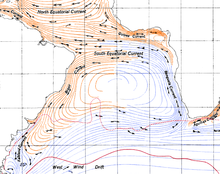
The Agulhas Current is the western boundary current of the southwest Indian Ocean. It flows south along the African east coast and along the south-eastern edge of the bank. It then retroflects back into the Indian7 Ocean south-west of the bank. This retroflection results in intense eddy activities such as meanders, eddies, and filaments.[7] In upper layer water, the Agulhas rings and eddies move warm and salty water into the large South Atlantic gyre, which exports it to the tropics. In the lower ocean layers water is transported in the opposite direction.[8]
The Agulhas acts as an oceanic convergence zone. Due to mass continuity this drives surface waters down, resulting in the upwelling of cold, nutrient rich water south of the current. Additionally, the convergence tends to increase the concentration of plankton in and around the Agulhas. Both of these factors result in the area being one of enhanced primary productivity as compared to the surrounding waters. This is especially notable in the Agulhas Retroflection waters, where chlorophyll-a concentrations tend to be significantly higher than the surrounding South Indian Ocean and South Atlantic Ocean waters.[9] Warm core rings are known to have lower primary productivity than surrounding cold waters. Agulhas Rings have been observed to carry waters with low chlorophyll-a concentration into the South Atlantic. The size of phytoplankton in Agulhas Rings tends to be smaller than in the surrounding water (around 20 μm in diameter).[9] Agulhas Rings have also been observed as removing larval and juvenile fish from the continental shelf.
The Benguela Current is the broad, northward flowing ocean current that forms the eastern portion of the South Atlantic Ocean gyre. The current extends from roughly Cape Point in the south, to the position of the Angola-Benguela front in the north, at around 16°S. The current is driven by the prevailing south easterly trade winds. Inshore of the Benguela Current proper, the south easterly winds drive coastal upwelling, forming the Benguela Upwelling System . The cold, nutrient rich waters that upwell from around 200–300 m depth in turn fuel high rates of phytoplankton growth, and sustain the productive Benguela ecosystem.
Upwellings

Upwelling is an oceanographic phenomenon that involves wind-driven motion of surface water away from the coast, which is replaced by a flow of deeper dense, cooler, and usually nutrient-rich water towards the ocean surface, The nutrient-rich upwelled water stimulates the growth and reproduction of primary producers such as phytoplankton. Due to the biomass of phytoplankton and presence of cool water in these regions, upwelling zones can be identified by cool sea surface temperatures (SST) and high concentrations of chlorophyll-a.[10][11] The increased availability of nutrients in upwelling regions results in high levels of primary production. Upwellings that are driven by coastal currents or diverging open ocean have the greatest impact on nutrient-enriched waters and global fishery yields.[12][9]
Ecological regions

The marine ecoregions of the South African exclusive economic zone are a set of geographically delineated regions of similar ecological characteristics on a fairly broad scale, covering the exclusive economic zone along the South African coast. There were originally five inshore bioregions over the continental shelf and four offshore bioregions covering the continental slope and abyssal regions. These bioregions are used for conservation research and planning. They were defined in the South African National Spatial Biodiversity Assessment of 2004.[4] The South African National Spatial Biodiversity Assessment of 2011 amended this to reduce the number of regions to four inshore and two offshore and rename them as ecoregions.[5]
Habitat types
A total of 136 marine habitat types have been identified. These include 37 coastal habitat types, 17 inshore habitat types in the 5 to 30 m depth range, 62 offshore benthic habitat types deeper than 30 m, and 16 offshore pelagic habitat types,[13] three types of island and one type of lagoon.[5]
Endemism
Endemism is the ecological state of a species or other taxonomic group being native to a single defined geographic location, such as an island, country or other defined zone, or habitat type; organisms that are indigenous to a place are not endemic to it if they are also found elsewhere. The extreme opposite of an endemic species is one with a cosmopolitan distribution, having a global or widespread range. Although the specific drivers of endemism are unclear, physical, climatic and biological factors can contribute to endemism. Endemic species can easily become endangered or extinct if their already restricted habitat changes, particularly—but not only—due to human actions, including the introduction of new species.
Over 13000 species of marine organisms are recorded from South African waters. Endemism is estimated at between 26 and 33%, the third highest marine endemism after New Zealand (51%) and Antarctica (45%). This varies between taxonomic groups from no endemic marine mammals or birds, to over 90% of chitons.[2]: 20
The region of highest known endemism is the south coast Agulhas inshore ecoregion, which is relatively far from the national borders, and relatively isolated from large scale oceanic circulation due to the effects of the widening of the continental shelf at the Agulhas Bank on the path of the Agulhas current, and far from other warm temperate regions. This region is largely bypassed by the Agulhas current, and has cooler inshore water due to upwelling, making it less hospitable to tropical Indo-west Pacific species. It is also isolated from the South Atlantic and Southern Ocean, so has been more prone to niche speciation.[2]: 20
Species lists
National
Marine animals
- List of comb jellies of South Africa
- List of echinoderms of South Africa
- List of marine and coastal birds of South Africa
- List of marine arthropods of South Africa
- List of marine bristleworms of South Africa
- List of marine bryozoans of South Africa
- List of marine cnidarians of South Africa
- List of marine fishes of South Africa
- List of marine flatworms of South Africa
- List of marine mammals of South Africa
- List of marine molluscs of South Africa
- List of marine reptiles of South Africa
- List of sponges of South Africa
Seaweeds
- List of green seaweeds of South Africa
- List of brown seaweeds of South Africa
- List of red seaweeds of South Africa
Prokaryotes
Regional
- List of marine animals of the Cape Peninsula and False Bay
- Seaweeds of the Cape Peninsula and False Bay
Economic value
Protection
Biodiversity protection is one of the priorities of the network of marine protected areas of South Africa.[14]
A marine protected area of South Africa is an area of coastline or ocean within the exclusive economic zone (EEZ) of the Republic of South Africa that is protected in terms of specific legislation for the benefit of the environment and the people who live in it and use it.[15] An MPA is a place where marine life can thrive under less pressure than unprotected areas, like underwater parks, and this healthy environment can benefit neighbouring areas.[16][17]
There are a total of 45 marine protected areas in the South African EEZ, with a total area of 5% of the waters as of 2019. The target was to have 10% of the oceanic waters protected by 2020. All but one of the MPAs are in the exclusive economic zone off continental South Africa, and one is off Prince Edward Island in the Southern Ocean.
People can take part in a wide range of non-consumptive activities in all of South Africa's MPAs, and some parts of some MPAs are zoned for limited consumptive activities.[17] Some of these activities require a permit, which is a form of taxation.
Threats
Research organisations
- Council for Scientific and Industrial Research (CSIR) – South African scientific research and development organisation
- Iziko South African Museum – South African national museum in Cape Town
- South African Association for Marine Biological Research – Non profit conservation research organisation based in Durban, SA
- South African Environmental Observation Network (SAEON) – A network to perform long-term ecological research in South Africa and surrounding waters
- South African Institute for Aquatic Biodiversity (SAIAB) – Centre for the study of aquatic biodiversity in Grahamstown, South Africa
- South African National Biodiversity Institute (SANBI) – Institution under the South African Department of Environmental Affairs
Publications
Books
Field guides:
- Lara Atkinson; Kerry Sink (2018). Atkinson, LJ; Sink, KJ (eds.). Field Guide to the Offshore Marine Invertebrates of South Africa (PDF). Pretoria: Malachite Marketing and Media. doi:10.15493/SAEON.PUB.10000001.
- Branch, G.M.; Branch, M.L. (1985). The Living Shores of Southern Africa (3rd impression ed.). Cape Town: C. Struik. ISBN 0-86977-115-9.
- Branch, G.M.; Branch, M.L.; Griffiths, C.L.; Beckley, L.E. (2010). Two Oceans: a guide to the marine life of southern Africa (2nd ed.). Cape Town: Struik Nature. ISBN 978-1-77007-772-0.
- Day, J.H. (1969). A guide to marine life on South African shores. Cape Town: Balkema.
- De Clerck, O.; Bolton, J.J.; Anderson, R. J.; Coppejans, E. (2005). Guide to the Seaweeds of KwazZulu-Natal. Scripta Botanica Belgica Volume 33. Joint publication of: National Botanical gardens of Belgium, VLIZ Flanders Marine Institute and Flemish Community. ISBN 90-72619-64-1.
- Gosliner, T.M. (1987). Nudibranchs of Southern Africa. ISBN 0-930118-13-8.
- Jones, Georgina (2008). A field guide to the marine animals of the Cape Peninsula. Cape Town: SURG. ISBN 978-0-620-41639-9.
- Heemstra, Phil; Heemstra, Elaine (2004). Coastal Fishes of Southern Africa. NISC/SAIAB. ISBN 1920033017.
- Kilburn, R.; Rippey, E. (1982). Sea Shells of Southern Africa. Macmillan. ISBN 0-86954-094-7.
- King, Dennis (1996). Reef fishes and corals: East coast of southern Africa. Cape Town: Struik. ISBN 1-86825-981-1.
- King, D.; Fraser, V. (2001). More Reef Fishes and Nudibranchs. Cape Town: Struik. ISBN 1-86872-686-X.
- King, Dennis; Fraser, Valda (2014). The Reef Guide: East and South Coasts of Southern Africa. Cape Town: Struik Nature. ISBN 9781775840183.
- Liltved, William Rune (2000). Cowries and their relatives of southern Africa: A study of the southern African Cypraeacean and Velutinacean gatropod fauna (2nd ed.). Gordon Verhoef, Seacomber Publications. ISBN 0908-42089-7.
- Smith, Margaret M; Heemstra, P., eds. (2003). Smith's sea fishes. Cape Town: Struik. ISBN 1-86872-890-0.
- Smith, J.L.B.; Smith, Margaret M. (1966). Fishes of the Tsitsikamma Coastal National Park. Johannesburg: Swan Press.
- Stegenga, H.; Bolton, J.J.; Anderson, R.J. (1997). Seaweeds of the South African West Coast. Contributions from the Bolus Herbarium, University of Cape Town. ISBN 0-7992-1793-X.
- Steyn, D.G.; Lussi, M. (2005). Offshore Shells of Southern Africa. ISBN 0-620-33607-2.
- Zsilavecz, Guido (2005). Coastal fishes of the Cape Peninsula and False Bay: A divers' identification guide. Cape Town: SURG. ISBN 0-620-34230-7.
- Zsilavecz, G. (2007). Nudibranchs of the Cape Peninsula and False Bay. Cape Town: SURG. ISBN 978-0-620-38054-6.
Journals
Reports
- South African National Spatial Biodiversity Assessment 2004
- Summary Report
- Driver, A., Maze, K., Lombard, A.T., Nel, J., Rouget, M., Turpie, J.K., Cowling, R.M., Desmet, P., Goodman, P., Harris, J., Jonas, Z., Reyers, B., Sink, K. & Strauss, T. 2004. South African National Spatial Biodiversity Assessment 2004: Summary Report. Pretoria: South African National Biodiversity Institute.
- Technical Reports
- Volume 3: Estuary Component
- Turpie, J.K. 2004. South African National Spatial Biodiversity Assessment 2004: Technical Report. Volume 3: Estuary Component. Pretoria: South African National Biodiversity Institute.
- Volume 4: Marine Component
- Lombard, A.T.; Strauss, T.; Harris, J.; Sink, K.; Attwood, C.; Hutchings, L. (2004). South African National Spatial Biodiversity Assessment 2004: Technical Report (PDF) (Report). Vol. 4: Marine Component. Pretoria: South African National Biodiversity Institute.
- Volume 3: Estuary Component
- Summary Report
- National Biodiversity Assessment 2011
- Volume 4: Marine and coastal component
- Sink, K; Holness, S; Harris, L; Majiedt, P; Atkinson, L; Robinson, T; Kirkman, S; Hutchings, L; Leslie, R; Lamberth, S; Kerwath, S; von der Heyden, S; Lombard, A; Attwood, C; Branch, G; Fairweather, T.; Taljaard, S.; Weerts, S.; Cowley, P.; Awad, A.; Halpern, B.; Grantham, H; Wolf, T. (2012). National Biodiversity Assessment 2011: Technical Report (PDF) (Report). Vol. 4: Marine and Coastal Component. Pretoria: South African National Biodiversity Institute.
- Volume 4: Marine and coastal component
- National Biodiversity Assessment for 2018
- Volume 3: Estuarine Realm
- Van Niekerk, Lara; Adams, Janine; Stephen, Lamberth; MacKay, Fiona; Taljaard, Suzan; Turpie, Jane; Weerts, Steven; Raimondo, Domitiila, C (29 September 2019). South African National Biodiversity Assessment 2018: Technical Report (Report). Vol. 3: Estuarine Realm. SANBI. hdl:20.500.12143/6373.
{{cite report}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link)
- Van Niekerk, Lara; Adams, Janine; Stephen, Lamberth; MacKay, Fiona; Taljaard, Suzan; Turpie, Jane; Weerts, Steven; Raimondo, Domitiila, C (29 September 2019). South African National Biodiversity Assessment 2018: Technical Report (Report). Vol. 3: Estuarine Realm. SANBI. hdl:20.500.12143/6373.
- Volume 4: Marine realm
- Sink, Kerry, J; Van der Bank, Megan; Majiedt, Prideel; Harris, Linda; Atkinson, Lara; Kirkman, Stephen; Karenyi, Natasha (29 September 2019). South African National Biodiversity Assessment 2018 Technical Report (Report). Vol. 4: Marine Realm. South African National Biodiversity Institute. hdl:20.500.12143/6372.
{{cite report}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link)
- Sink, Kerry, J; Van der Bank, Megan; Majiedt, Prideel; Harris, Linda; Atkinson, Lara; Kirkman, Stephen; Karenyi, Natasha (29 September 2019). South African National Biodiversity Assessment 2018 Technical Report (Report). Vol. 4: Marine Realm. South African National Biodiversity Institute. hdl:20.500.12143/6372.
- Volume 3: Estuarine Realm
See also
- Biodiversity – Variety and variability of life forms
- Ecology – Study of organisms and their environment
- Marine biodiversity – The variety of living organisms that live in the seas
- Marine biology – Scientific study of organisms that live in the ocean
- Marine protected areas of South Africa – Protected areas of coastline or ocean in the EEZ of South Africa
References
- ^ "Tenfold increase in marine protected areas supports SA'S sustainable oceans economy". www.sanbi.org. 7 October 2019. Retrieved 30 August 2020.
- ^ a b c d e Sink, Kerry, J; Van der Bank, Megan; Majiedt, Prideel; Harris, Linda; Atkinson, Lara; Kirkman, Stephen; Karenyi, Natasha (29 September 2019). South African National Biodiversity Assessment 2018 Technical Report (Report). Vol. 4: Marine Realm. South African National Biodiversity Institute. hdl:20.500.12143/6372.
{{cite report}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ "National Biodiversity Assessment". www.sanbi.org. 4 March 2018. Retrieved 14 February 2019.
- ^ a b Lombard, A.T.; Strauss, T.; Harris, J.; Sink, K.; Attwood, C.; Hutchings, L. (2004). South African National Spatial Biodiversity Assessment 2004: Technical Report (PDF) (Report). Vol. 4: Marine Component. Pretoria: South African National Biodiversity Institute.
- ^ a b c Sink, K; Holness, S; Harris, L; Majiedt, P; Atkinson, L; Robinson, T; Kirkman, S; Hutchings, L; Leslie, R; Lamberth, S; Kerwath, S; von der Heyden, S; Lombard, A; Attwood, C; Branch, G; Fairweather, T.; Taljaard, S.; Weerts, S.; Cowley, P.; Awad, A.; Halpern, B.; Grantham, H; Wolf, T. (2012). National Biodiversity Assessment 2011: Technical Report (PDF) (Report). Vol. 4: Marine and Coastal Component. Pretoria: South African National Biodiversity Institute. p. 325. Note: This is the full document, with numbered pages.
- ^ "2018 National Biodiversity Assessment". biodiversityadvisor.sanbi.org. Retrieved 30 August 2020.
- ^ Blanke, B.; Penven, P.; Roy, C.; Chang, N.; Kokoszka, F. (2009). "Ocean variability over the Agulhas Bank and its dynamical connection with the southern Benguela upwelling system" (PDF). Journal of Geophysical Research. 114 (C12028): Introduction, pp. 1–2. Bibcode:2009JGRC..11412028B. doi:10.1029/2009JC005358. Retrieved 2 January 2015.
- ^ Ruijter, W. P. M., de; Cunningham, S. A.; Gordon, A. L.; Lutjeharms, J. R. E.; Matano, R. P.; Piola, A. R. (2003). "On the South Atlantic Climate Observing System (SACOS)" (PDF). Report of the CLIVAR/OOPC/IAI Workshop: 45. Retrieved 4 January 2015.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ a b c Mann, K. H.; Lazier, J.R. (2006). Dynamics of Marine Ecosystems: Biological-Physical Interactions in the Oceans (3rd ed.). Blackwell Publishing. ISBN 978-1405111188.
- ^ Anderson, DM; Prell, WL (1993). "A 300 KYR record of upwelling off Oman during the late quaternary: evidence of the Asian southwest monsoon". Paleoceanography. 8 (2): 193–208. Bibcode:1993PalOc...8..193A. doi:10.1029/93pa00256.
- ^ Sarhan, T; Lafuente, JG; Vargas, M; Vargas, JM; Plaza, F (1999). "Upwelling mechanisms in the northwestern Alboran Sea". Journal of Marine Systems. 23 (4): 317–331. doi:10.1016/s0924-7963(99)00068-8.
- ^ Jennings, S.; Kaiser, M.J.; Reynolds, J.D. (2001). Marine Fisheries Ecology. Oxford: Blackwell Science Ltd. ISBN 0-632-05098-5.
- ^ Sink, K.; Holness, S.; Harris, L.; Majiedt, P; Atkinson, L; Robinson, T; Kirkman, S; Hutchings, L.; Leslie, R; Lambeth, S; Kerwath, S; von der Heyden, S; Lombard, A; Attwood, C.; Branch, G.; Fairweather, T.; Taljaard, S.; Weerts, S.; Cowley, P.; Awad, A.; Halpern, B.; Grantham, H; Wolf, T. (2012). National Biodiversity Assessment 2011: Technical Report (PDF) (Report). Vol. 4: Marine and Coastal Component. Pretoria: South African National Biodiversity Institute. Key findings. Note: This is the executive summary
- ^ "Government Notices - Department of Environmental Affairs". Regulation Gazette No. 10553. 608 (39646). Pretoria: Government Printer. 3 February 2016.
- ^ "Protecting the ocean". www.marineprotectedareas.org.za. Retrieved 18 January 2019.
- ^ "Marine Protected Areas". www.saambr.org.za. Retrieved 16 May 2019.
- ^ a b Mann-Lang, Judy; Mann, Bruce; Sink, Kerry, eds. (September 2018). "Fact sheet 3: Marine Protected Areas" (PDF). SAAMBR. Retrieved 15 May 2019.
- v
- t
- e
- Afrotropical realm
- Marine biodiversity of South Africa
- Temperate Southern Africa
- Western Indo-Pacific
- Wildlife of South Africa
National taxon checklists | |||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| |||||||||||||||||||||
|
| |||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||
Biodiversity research in SA | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| |||||||||||
Related | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| |||||||
 Categories: Biodiversity of South Africa
Categories: Biodiversity of South Africa
- Index












