Heuston railway station
- Bus Eireann
- Citylink
- Dublin Bus
- Dublin Express
- Go-Ahead Ireland
- JJ Kavanagh and Sons
- Martley’s
- M4 Direct
- 4
- 22
- 26
- 51D
- 52
- 60
- 115
- 120
- 120B
- 120F
- 120X
- 126
- 126A
- 126D
- 126T
- 126X
- 130
- 145
- 245X
- 707
- 717
- 735
- 736
- 763
- 782
- 824
- 842
- 845
- 847
- C1
- C2
- C3
- C4
- C5
- C6
- S2
- P29
- X25
- X26
- X27
- X28
- X30
- X31
- X32
- Red Line
John MacNeill (train shed)[1][2]
 19,750
19,750 19,544
19,544 22,296
22,296 23,165
23,165 22,836
22,836Location | |
|---|---|
  Dublin Heuston Location within Ireland Show map of Ireland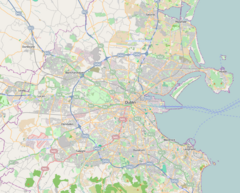  Dublin Heuston Dublin Heuston (Dublin) Show map of Dublin  Dublin Heuston Dublin Heuston (Central Dublin) Show map of Central Dublin |
Notes | |
|---|---|
Passenger numbers are for a single day of usage in the year mentioned, and are the sum of the year's boardings and alightings. Source:[4] |
Dublin–Cork | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Legend | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Dublin to Galway/Westport | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Legend | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Dublin–Waterford | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Legend | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
South Western Commuter | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Legend | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||


Heuston Station, (/ˈhjuːstən/ ⓘ HEW-stən; Irish: Stáisiún Heuston; formerly Kingsbridge Station) also known as Dublin Heuston, is one of Dublin's largest railway stations and links the capital with the south, southwest and west of Ireland. It is operated by Iarnród Éireann (IÉ), the national railway operator. It also houses the head office of its parent company, Córas Iompair Éireann (CIÉ).[5] The station is named in honour of Seán Heuston, an executed leader of the 1916 Easter Rising, who had worked in the station's offices.
History
In 1836, a committee of Commissioners was appointed by the British Government to identify a system of rail routes throughout Ireland which would best serve the interests of the country as a whole.[6] In their report of 1838, Kingsbridge, or 'King's Bridge', was selected as the optimum location for a terminus in Dublin which would most conveniently serve a main trunk railway line to the southern and western districts of Ireland.[6] The site had been known as Kingsbridge since the completion of the nearby King's Bridge over the River Liffey in 1828.[7]
The Great Southern and Western Railway (GS&WR) company was authorised by an Act passed in 1844 and began selecting a site in Dublin for their main city terminus, as well as the site of their headquarters.[6] In a series of pamphlets, the promoters of a proposed rail link to Cashel, County Tipperary argued that Kingsbridge was the better choice for a Dublin terminus over a competing proposal for a Portobello terminus, due to it being conveniently located next to the quays, Smithfield cattle market, hay and straw markets, wool and butter cranes, woollen, cotton, iron and leather warehouses, the Linenhall area, as well as sites of strategic military importance such as the Royal Barracks.[6]
An Incorporation Act entitled “An Act for Making and Maintaining a Railway from the City of Dublin to the Town of Cashel, with a Branch to the Town of Carlow" was passed and established in law.[6] On 28 October 1845 the Great Southern and Western Railway Company bought a site in Dublin adjoining the Military Road, and another parcel of ground, from the Right Honorable Henry John Lord Viscount Palmerston for £1,600.[a] In December 1845 the GS&WR began advertising for tenders for building the Kingsbridge railway terminus on the land they had recently bought.[6]
The station opened on 4 August 1846 as the terminus and headquarters of the Great Southern and Western Railway with the Freeman's Journal describing how "carriages of all classes were densely crowded with passengers, thus giving early evidence of the vast traffic which is likely to accrue on the line when in full and perfect operation".[6] The first regular passenger train service from the station commenced later that month with the running of two trains each way daily between Dublin and Carlow (Carlow-bound trains departed Dublin at 9am and 5pm).[6] Trains were scheduled to take about 2hr 35min for the 56 mi (90 km) stretch to Carlow from where conventional mail coach connections could carry passengers onwards to Kilkenny, Clonmel, Waterford or Cork.[8]
The passenger terminal and buildings were built to designs by London-born architect Sancton Wood, and the train sheds and infrastructure were designed by Irish-born railway engineer John MacNeill.[1] Regarding the architectural merits of the passenger terminal, historian Maurice Craig described it thus: "a delightful building, a renaissance palazzo, gay and full-blooded, with fruity swags and little domed towers on the wings, a thoroughgoing formal composition, excellently articulated".[9]
When first constructed the station had only two platforms separated by 5 carriage lines. Two of the lines were subsequently replaced by a two-sided platform and the remaining carriage line also removed. An additional platform, created in 1872 on the south side of the station, beyond the station roof, was known as the "military platform" - the intention being that military personnel could be kept separate from the rest of the public.[10] Due to the need to cater for increased demand and reduce delays, three new platforms were incorporated in August 2002 as part of a €170,000,000 development incorporating improved signalling and approach track-work.[11]
In 1966, on the 50th anniversary of the Easter Rising, it was renamed "Heuston Station" in honour of Seán Heuston, a young railway worker who commanded a nearby post in the 1916 Easter Rising. Heuston was one of the 16 executed by the British after that Rising, and had previously worked in the station's offices.[7]
Since the station's refurbishment and modernisation (by Quinn Savage Smyth architects and engineers Buro Happold)[12] its retail facilities now include a branch of Easons, as well as some dining facilities, including a branch of Supermacs, several cafés, a kiosk, and a large pub.[13]
A maintenance depot at the Inchicore railway works is located approximately three kilometres (two miles) away and, as with Heuston Station itself, was also opened in 1846.[14]
Operation
Based on 2019 National Transport Authority figures for "boardings and alightings", Heuston was then the third busiest station in Ireland, behind Connolly and Pearse stations, also in Dublin.[4] All services leave the station on a triple line as far as Inchicore, quadruple line until Hazelhatch, and thereafter only double line (one each way).[citation needed]
Rail services
The following services depart Heuston on weekdays:[15][needs update]
- 1 train per hour (tph) to Cork Kent[15]
- 7 trains per day (tpd) to Waterford Plunkett[16]
- 1 tp2h to Galway Ceannt[17]
- 3 tpd to Westport[18]
- 1 tph to Limerick Colbert (peak times only)[15]
- 1 tpd to Tralee Casement[15]
- 1 tph to Portlaoise[15]
- 1 tpd to Carlow[15]
- 1 tpd to Athlone[15]
Heuston is the terminus for the mainline to Cork, and there are key service and transfer points in the Cork-bound direction at:
- Kildare (for stations on the Waterford line)
- Portarlington (for routes to the west via Tullamore and Athlone)
- Portlaoise (end of commuter services from Heuston)
- Ballybrophy (junction for stations on the Limerick-Ballybrophy railway line),
- Limerick Junction (for transfer to Limerick and Ennis services, and Waterford via Clonmel)
- Mallow (junction for Killarney and Tralee, and the start of Cork commuter services).
| Preceding station |  Iarnród Éireann Iarnród Éireann | Following station | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Terminus | InterCity Dublin-Cork | Portlaoise or Thurles | ||
| Terminus | InterCity Dublin-Waterford railway line | Hazelhatch and Celbridge or Newbridge | ||
| Terminus | InterCity Dublin-Limerick via Thurles | Kildare | ||
| Terminus | InterCity Dublin–Westport/Galway railway line | Sallins and Naas or Portarlington | ||
| Terminus | InterCity Ballina branch line | Portarlington | ||
| Terminus | InterCity Mallow–Tralee line | Ballybrophy | ||
| Terminus | Commuter South Western Commuter | Park West & Cherry Orchard | ||
Links to other main railway stations
Before 2016, the physical rail link between Connolly Station and Heuston via the Phoenix Park Tunnel was usually only used for freight and rolling stock movements. Once or twice a year special trains operated, usually from Cork to Connolly for Gaelic Athletic Association matches at Croke Park. A more regular service along this route began on 21 November 2016.[19]
The Luas light rail red line connects the two stations (apart from off-peak Saturdays, Sundays and bank holidays).[20] Dublin Express has a direct service to Dublin Airport.[citation needed]
Platforms
There are nine platforms: eight terminal platforms and one through platform. Platform 1 is an extension to Platform 2, and is reachable only via that platform. Prior to Heuston's 2002-2004 upgrade, there were five terminal platforms.[21][22]
The through platform is numbered Platform 10 and is situated on the Phoenix Park Tunnel line, which connects to Connolly Station.[22] There is no platform nine.[22] Platform 10 is some distance from the main concourse and is not used for any regularly scheduled trains.
Proposed developments
A 2018 consultation paper for the proposed Dublin MetroLink project included a reference to a potential future station, labelled "Heuston West", with connections via the Phoenix Park Tunnel to Cabra.[23]
Other plans, first published in the 1970s,[24][25] suggested that a proposed DART Underground project would link underground stations at Heuston and Pearse Street via a tunnel.[26][27] As of 2015, these plans were subject to review,[27] and as of mid-2018, the DART Underground project was not funded.[28]
Heuston Luas stop
Heuston  | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
 A tram at Heuston in 2005 | |||||||||||
| General information | |||||||||||
| Location | Dublin Ireland | ||||||||||
| Coordinates | 53°20′48″N 6°17′30″W / 53.34665°N 6.2916934°W / 53.34665; -6.2916934 | ||||||||||
| Owned by | Transdev | ||||||||||
| Operated by | Luas | ||||||||||
| Line(s) | Red | ||||||||||
| Platforms | 3 | ||||||||||
| Construction | |||||||||||
| Structure type | At-grade | ||||||||||
| Other information | |||||||||||
| Fare zone | Central/Red 2 | ||||||||||
| Key dates | |||||||||||
| 26 September 2004 | Station opened | ||||||||||
| Services | |||||||||||
| |||||||||||
| |||||||||||
 Luas Red Line Luas Red Line | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Legend | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Heuston is an interchange with Dublin's Luas light rail tram system. Opened in 2004,[29] Heuston Luas stop is located in front of the station building; the tram tracks run perpendicular to the main line tracks. To the north of the stop, trams cross the River Liffey on the Seán Heuston Bridge, which was refurbished as part of the Luas construction. To the south, trams travel up Steeven's Lane, which is closed to road vehicles other than those accessing St. Patrick's University Hospital.[30]
Heuston has three platforms. There are two outer edge platforms and two sides of an island platform. The two platforms nearest the station serve the same section of track, used for northbound trams travelling towards Connolly or The Point. The platform nearest St. John's Road West is for southbound trams travelling towards Tallaght and Saggart. The eastern side of the island is a terminus platform, used only in certain peak times, when extra services are run in the city centre section.
In culture
Exterior shots of the station appeared in the 1978 heist film The First Great Train Robbery purporting to be London Bridge railway station. The station was altered to represent the Victorian era including the erection of offices, signs, posters and horse-drawn transport.[31]
Gallery
-
 Facade in 2018
Facade in 2018 -
 Cork-Dublin train at Heuston
Cork-Dublin train at Heuston -
 Renovated roof
Renovated roof -
 Heuston interior
Heuston interior -
 Luas at Heuston
Luas at Heuston
See also
Notes
- ^ Registry of Deeds, Dublin. 1847-20-179. Registered 21/12/1847. A Memorial of an Indented Deed of Conveyance bearing date the Twenty eighth day of October in the year of our Lord one thousand eight hundred and forty five made between the Right Honorable (sic) Henry John Lord Viscount Palmerston of the Kingdom of Ireland of the one part and the Great Southern and Western Railway Company Ireland Incorporated by an Act of Parliament made and passed in the seventh and eighth years of the Reign of her present Majesty Queen Victoria intituled “An Act for making and maintaining a Railway from the city of Dublin to the Town of Cashel with a branch to the town of Carlow” of the other part Whereby the said Henry John Lord Viscount Palmerston in consideration of the sum of one thousand six hundred pounds paid to him by the said Great Southern and Western Railway Company the receipt of whereof was thereby acknowledged did convey, grant and release to the said Company, their successors and assigns All That or those the pieces or portions of land adjoining the Military Road situate in the Parish of Saint James in the City of Dublin and also All That and those the pieces or parcels of ground situate in the said Parish of Saint James and County of Dublin containing in the whole one acre and twenty two perches Irish plantation measure…
References
- ^ a b "1846 – Heuston Station, Dublin". Architecture of Dublin City. Archiseek. 2010. Archived from the original on 6 April 2019. Retrieved 29 November 2018.
- ^ "Rewind - Kingsbridge/Heuston Station". echo.ie. The Echo. 30 August 2018. Archived from the original on 29 November 2018. Retrieved 29 November 2018.
- ^ "Get All Stations". api.irishrail.ie. Irish Rail. Archived from the original on 17 November 2022. Retrieved 17 November 2022.
- ^ a b "National Rail Census Report 2019" (PDF). nationaltransport.ie. 2020. pp. 41, 45. Archived (PDF) from the original on 7 March 2021. Retrieved 24 February 2021.
- ^ "CIÉ Annual Report 2014" (PDF). cie.ie. CIÉ. Archived from the original (PDF) on 24 August 2015.
The [CIÉ] books of account are kept in Heuston Station, Dublin 8 [..] Secretary of the Board [..] Heuston Station, Dublin 8
- ^ a b c d e f g h Jacob, Wm. J. (1 June 1944). "Kingsbridge Terminus". Dublin Historical Record. 6 (3). Dublin: Old Dublin Society: 107–120. JSTOR 30105471.
- ^ a b Boyd-Hope, Gary; Beaumont, Jonathan (14 August 2017). "How The Railways Remembered Ireland's 1916 Easter Rising". Railway Magazine. Archived from the original on 15 April 2018. Retrieved 15 April 2018.
- ^ Murray & McNeill (1976), pp. 17.
- ^ Craig, p.322
- ^ Murray, K. A.; McNeil, D.B. (1976). The Great Southern & Western Railway. Irish Record Railway Society. pp. 170, 171. ISBN 0904078051.
- ^ "A New Improved Heuston Station 2002". rte.ie. RTÉ. 22 August 2002. Archived from the original on 22 November 2017. Retrieved 30 September 2018.
- ^ "Heuston Station". quinnarchitects.ie. Quinn Architects. 26 April 2012. Archived from the original on 29 November 2018. Retrieved 29 November 2018.
- ^ "M&S Simply Food Opens in Heuston Station". 98fm.ie. 98FM. 3 March 2017. Archived from the original on 29 November 2018. Retrieved 29 November 2018.
- ^ "Inchicore Railway Works, Dublin 8, Dublin City". buildingsofireland.ie. National Inventory of Architectural Heritage. Archived from the original on 29 November 2018. Retrieved 29 November 2018.
- ^ a b c d e f g "Dublin – Cork - Full service to/from Intermediate Stations" (PDF). irishrail.ie. Irish Rail. 26 September 2022. Archived from the original (PDF) on 16 November 2022. Retrieved 16 November 2022.
- ^ "Dublin - Waterford" (PDF). irishrail.ie. Irish Rail. Retrieved 16 November 2022.
- ^ "Dublin - Galway" (PDF). irishrail.ie. Irish Rail. Retrieved 16 November 2022.
- ^ "Dublin - Westport & Ballina" (PDF). irishrail.ie. Irish Rail.
- ^ "Plans for four trains an hour in Phoenix Park tunnel next year". The Herald. 9 March 2015. Archived from the original on 2 April 2015. Retrieved 18 March 2015.
- ^ "Luas - Red Line Frequency". luas.ie. Luas. Archived from the original on 30 November 2011.
- ^ "Heuston to have four new platforms". irishtimes.com. Irish Times. 15 February 2002. Archived from the original on 29 November 2018. Retrieved 29 November 2018.
Iarnrod Éireann is planning four new platforms for Heuston Station [..] The four new platforms will be added to the existing five
- ^ a b c "Heuston Re-development". irrs.ie. Irish Railway Record Society. 2002. Archived from the original on 31 October 2017.
- ^ "Metrolink Public Consultation Document" (PDF). data.tii.ie. Transport Infrastructure Ireland. 2018. Archived (PDF) from the original on 27 March 2018. Retrieved 29 November 2018.
- ^ "Whatever happened to... An underground rail line through Dublin's city centre?". thejournal.ie. The Journal. 3 August 2017. Archived from the original on 29 November 2018. Retrieved 29 November 2018.
- ^ "Could an underground Dart solve Dublin's traffic gridlock? It's being considered". thejournal.ie. The Journal. 5 February 2018. Archived from the original on 13 August 2018. Retrieved 8 August 2018.
the Dart Underground, previously known as the Interconnector [was] Originally conceived of in the 1972 Transportation in Dublin plan
- ^ "DART Underground Webpage". irishrail.ie. Irish Rail. Archived from the original on 3 March 2015.
- ^ a b DART Expansion Programme Business Case (PDF) (Report). Irish Rail. 24 April 2015. p. 46. Archived (PDF) from the original on 14 November 2017. Retrieved 29 November 2018.
On the basis of the issues raised [in 2008] during the design review, Iarnród Éireann [instead proposed] extending DART Underground to terminate within CIÉ lands at Inchicore as opposed to Heuston Station
- ^ "Office plan scrapped to facilitate shelved Dart Underground". irishtimes.com. Irish Times. 5 June 2018. Archived from the original on 2 September 2018. Retrieved 8 August 2018.
the [DART Underground] project having been shelved by the Government [in 2011, does] not have government funding [and] was not included in the 10-year National Development Plan published earlier [in 2018]
- ^ "Luas - Public Transport Integrated Ticketing System, RPA Railway Procurement Agency Ireland LUAS". Archived from the original on 28 February 2008.
- ^ "Heuston · Saint James' (Part of Phoenix Park), Dublin, Ireland".
- ^ McCormack, Stan (13 August 2020). "When the movies came to town". Westmeath Examiner. Retrieved 19 July 2022.
Sources
- Craig, Maurice (1952). Dublin 1660-1860: The Shaping of a City. Dublin: Liberties Press. ISBN 978-1905483112.
- Murray, K.A.; McNeill, D.B. (1976). Great Southern & Western Railway. Dublin: Irish Railway Record Society. ISBN 0-904078-05-1.
External links

- Irish Rail Dublin Heuston Station Website
- Luas Heuston Stop information