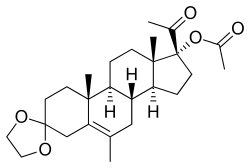
Edogestrone
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Other names | Edogesterone; PH-218; 17α-Acetoxy-3,3-ethylenedioxy-6-methylpregn-5-en-20-one |
| Drug class | Progestogen; Progestogen ester |
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number |
|
| PubChem CID |
|
| ChemSpider |
|
| UNII |
|
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) |
|
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C26H38O5 |
| Molar mass | 430.585 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) |
|
| |
InChI
| |
Edogestrone (INNTooltip International Nonproprietary Name, BANTooltip British Approved Name) (developmental code name PH-218), or edogesterone, also known as 17α-acetoxy-3,3-ethylenedioxy-6-methylpregn-5-en-20-one, is a steroidal progestin and antiandrogen of the 17α-hydroxyprogesterone group which was synthesized in 1964 but was never marketed.[1][2] Similarly to the structurally related steroid cyproterone acetate, edogestrone binds directly to the androgen receptor and antagonizes it, displacing androgens like testosterone from the receptor, though not as potently as cyproterone acetate.[3] The drug has also been found to suppress androgen production, likely via progesterone receptor activation-mediated antigonadotropic activity.[4]
See also
- Steroidal antiandrogen
- List of progestogens
- List of steroidal antiandrogens
- List of progestogen esters
References
- ^ Elks J (14 November 2014). The Dictionary of Drugs: Chemical Data: Chemical Data, Structures and Bibliographies. Springer. pp. 478–. ISBN 978-1-4757-2085-3.
- ^ Geller J, McCoy K (February 1974). "Biologic and biochemical effects of anti-androgens on rat ventral prostate". Acta Endocrinologica. 75 (2): 385–397. doi:10.1530/acta.0.0750385. PMID 4406552.
- ^ Spring-Mills E, Hafez ES (1 January 1980). Male accessory sex glands: biology and pathology. Elsevier/North-Holland Biomedical Press. p. 500. ISBN 9780444801678.
- ^ Castro JE (9 March 2013). The Treatment of Prostatic Hypertrophy and Neoplasia. Springer Science & Business Media. pp. 39–. ISBN 978-94-015-7190-6.
Geller has also demonstrated significant decreases in plasma or urine testosterone glucuronide levels following the administration of three other anti-androgens. These include Delalutin, Chlormadinone acetate, and PH-218. It would appear that decreased androgen production is a property shared by all anti-androgens to date.
- v
- t
- e
| Agonists |
|
|---|
- See also
- Receptor/signaling modulators
- Androgens and antiandrogens
- Estrogen receptor modulators
- Progesterone receptor modulators
- List of androgens and anabolic steroids
 | This article about a steroid is a stub. You can help Wikipedia by expanding it. |
- v
- t
- e
 | This drug article relating to the genito-urinary system is a stub. You can help Wikipedia by expanding it. |
- v
- t
- e










